本文由 MC A 建筑事务所 授权mooool发表,欢迎转发,禁止以mooool编辑版本转载。
Thanks Mario Cucinella Architects for authorizing the publication of the project on mooool. Text description provided by Mario Cucinella Architects.
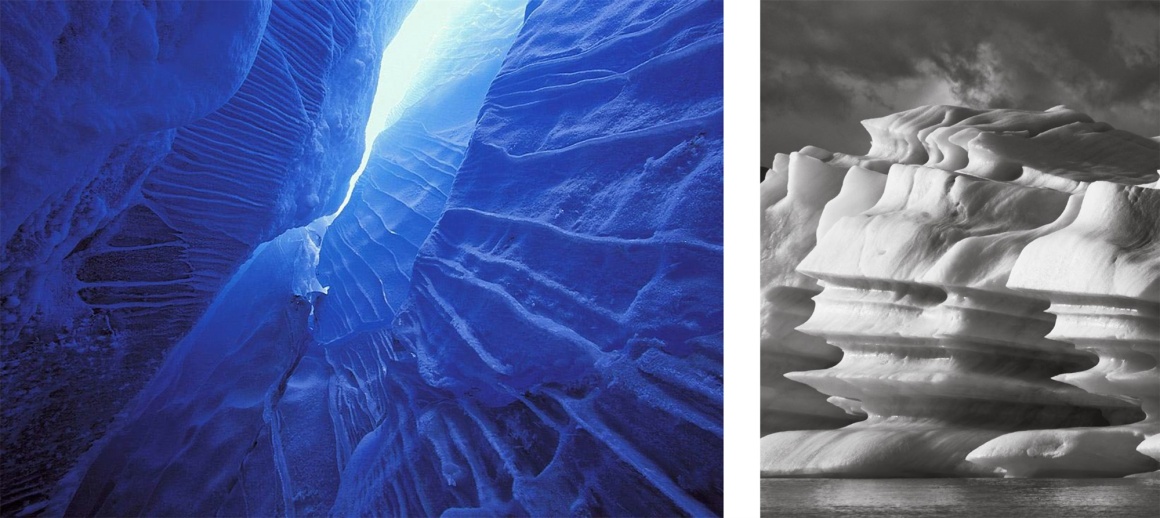
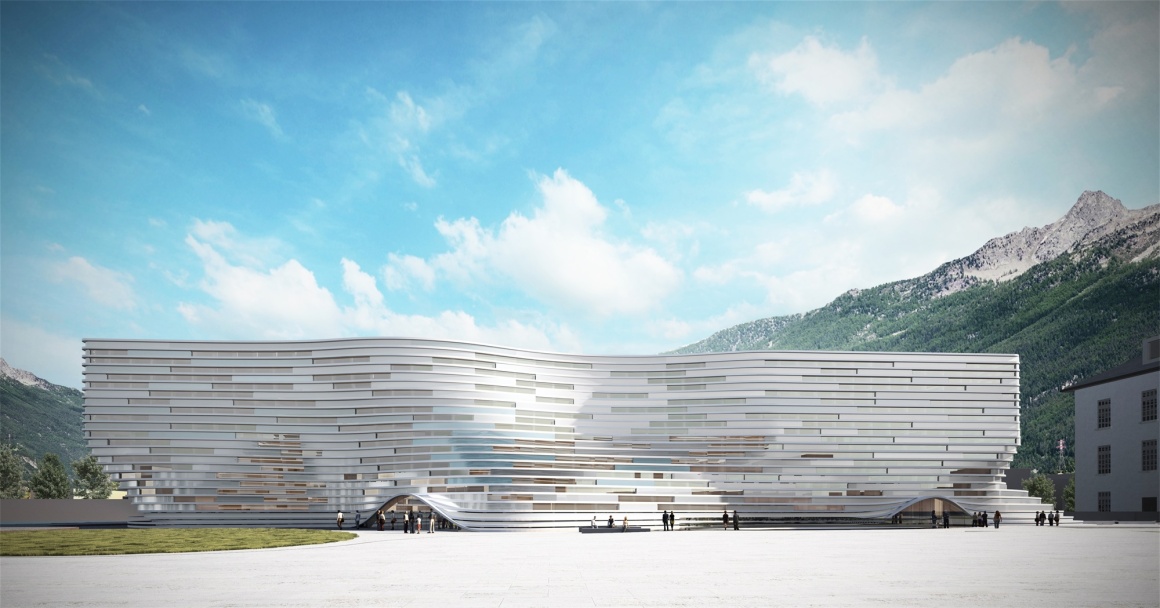
MC A:提到意大利的瓦莱达奥斯塔大区,人们立刻会想到切尔维尼亚、库马耶尔、皮拉…这些地方的滑雪场举世闻名,是众多滑雪、登山、滑冰爱好者的天堂。瓦莱达奥斯塔大区境内全部是山脉,遍布惊人的自然景观,同样也有具有丰富的传统文化宝藏。MC A从环境和人文可持续发展的角度出发,瓦莱达奥斯塔大学新校区的设计从层层叠叠的冰山形态中汲取灵感,融合自然生态景观,与当地白雪皑皑的高山相映衬,充分尊重当地自然环境和气候,彰显地域文化特色。
MC A: Speaking of Valle d’Aosta in Italy, people immediately think of Cervinia, Courmayeur, Pyla…the ski resorts in these places are world-famous, and the paradise for many skiing, mountaineering and skating lovers. The Valle d’Aosta region is full of mountains, amazing natural landscapes, and also rich in traditional cultural treasures. From the perspective of environmental and humanistic sustainable development, the design of the new campus of the University of Valle d’Aosta draws inspiration from layers of icebergs, integrates natural ecological landscapes, and contrasts with the local snow-capped mountains. Respect the local natural environment and climate, highlight the regional cultural characteristics.
同时通过创新的校园体系结构,考虑一系列城市与校园功能的联系,创建对环境和城市影响最小化的建筑,使其成为意大利首批零能源建筑和奥斯塔市现代城市化的地标。
e city and the function are considered to create buildings with minimal impact on the environment and the city, making it the first batch of zero-energy buildings in Italy and a landmark of modern urbanization in Aosta.
▼冰山设计概念启发 Design concept inspiration
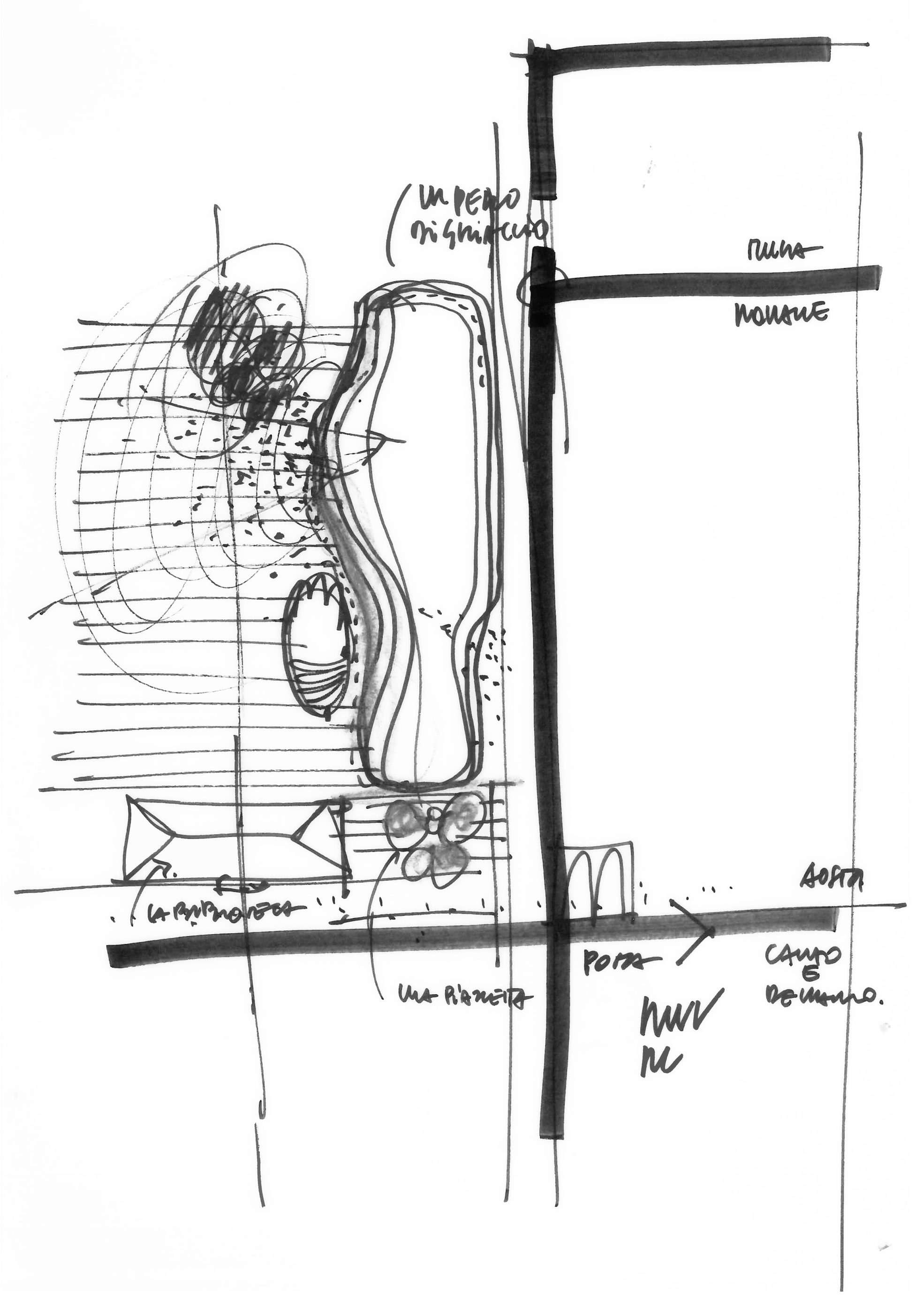
▼概念草图 Sketch
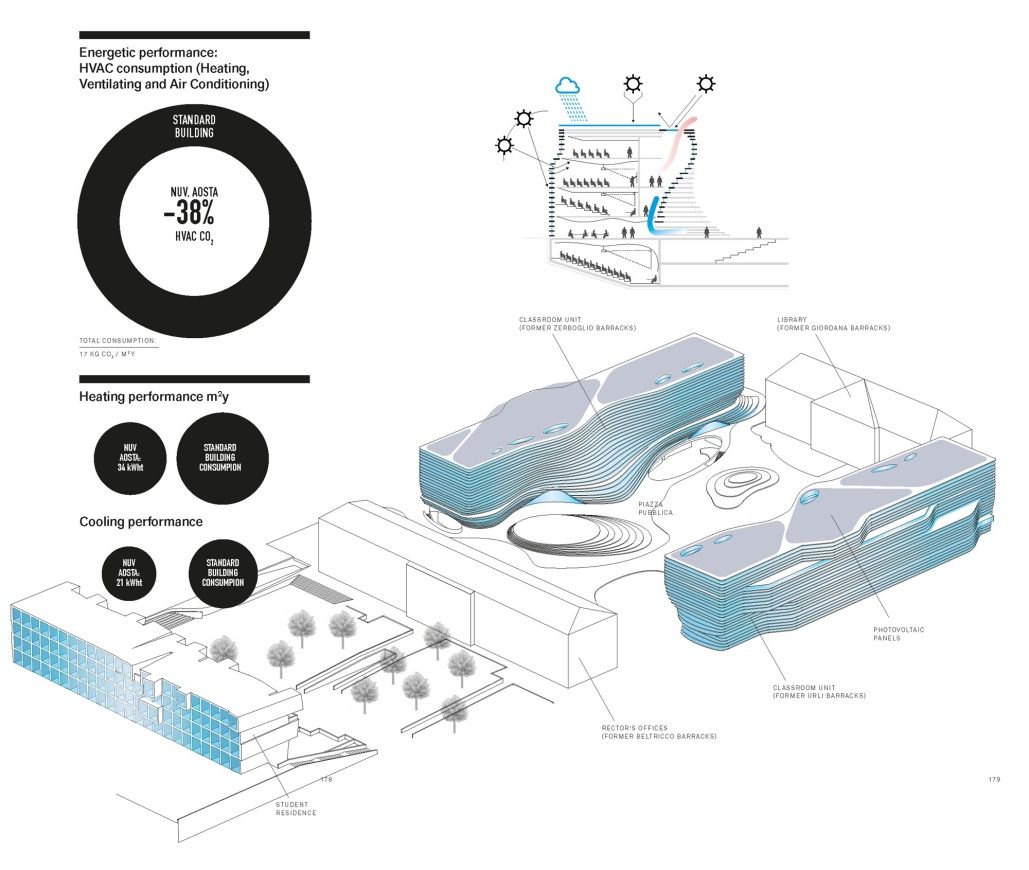
可持续性是新校区建设的重点,采取主动节能和被动措施多方面结合提高能源效率,节能技术的整合成功应对了各种挑战,相比同类建筑降低了最少38%的能耗。
从社会层面看,开放性的新校区,除了具有通常的校园功能外,还很好的承担和履行了社会责任。实现大学与所在环境的融合,建立校区与城市的和谐互动关系,优化城市结构,为历史中心注入新的活力。为奥斯塔社会及城市的可持续发展产生了重要作用。
新校区的设计从植物界汲取智慧,学习植物有机体独立但又相互关联的组织经验。新校园在加强文化氛围,扩大绿化面积,将其整合成贯穿全城的绿色综合系统的同时,也强调自主体系,使得每栋建筑物均具有功能自主权。
Sustainability is the focus of the construction of the new campus. Active energy-saving and passive measures are taken to improve energy efficiency. The integration of energy-saving technologies has successfully met various challenges and reduced energy consumption by at least 38% compared with similar buildings.
From a social perspective, the open new campus not only has the usual campus functions, but also fulfills its social responsibilities. Realize the integration of the university and the environment, establish a harmonious and interactive relationship between the campus and the city, optimize the urban structure, and inject new vitality into the historical center. It has played an important role in the sustainable development of Aosta society and the city.
The design of the new campus draws wisdom from the plant world, and learns the independent but interrelated organizational experience of plant organisms. While strengthening the cultural atmosphere, expanding the green area, and integrating it into a green comprehensive system throughout the city, the new campus also emphasizes an autonomous system so that each building has functional autonomy.
智慧校园 Smart Campus
瓦莱达奥斯塔大学新校区位于大区首府奥斯塔市中心,是前军营建筑群所在地。北以Monte Pasubio为边界,东到Monte Solarolo,南至共和广场,西达Monte Vodice。项目通过对新校区进行全新规划,创建城市开放校园。保护和改造具有重要历史意义的旧建筑,设计代表性的新建筑。
The new campus of the University of Valle d’Aosta is located in the center of the region’s capital, Aosta, where is he former military barrack . It is bordered by Monte Pasubio in the north, Monte Solarolo in the east, the Republic Square in the south, and Monte Vodice in the west. The project creates an open urban campus through a new planning . Preserve and renovate old buildings of important historical significance, and design representative new buildings.
▼总平面图 Master Plan
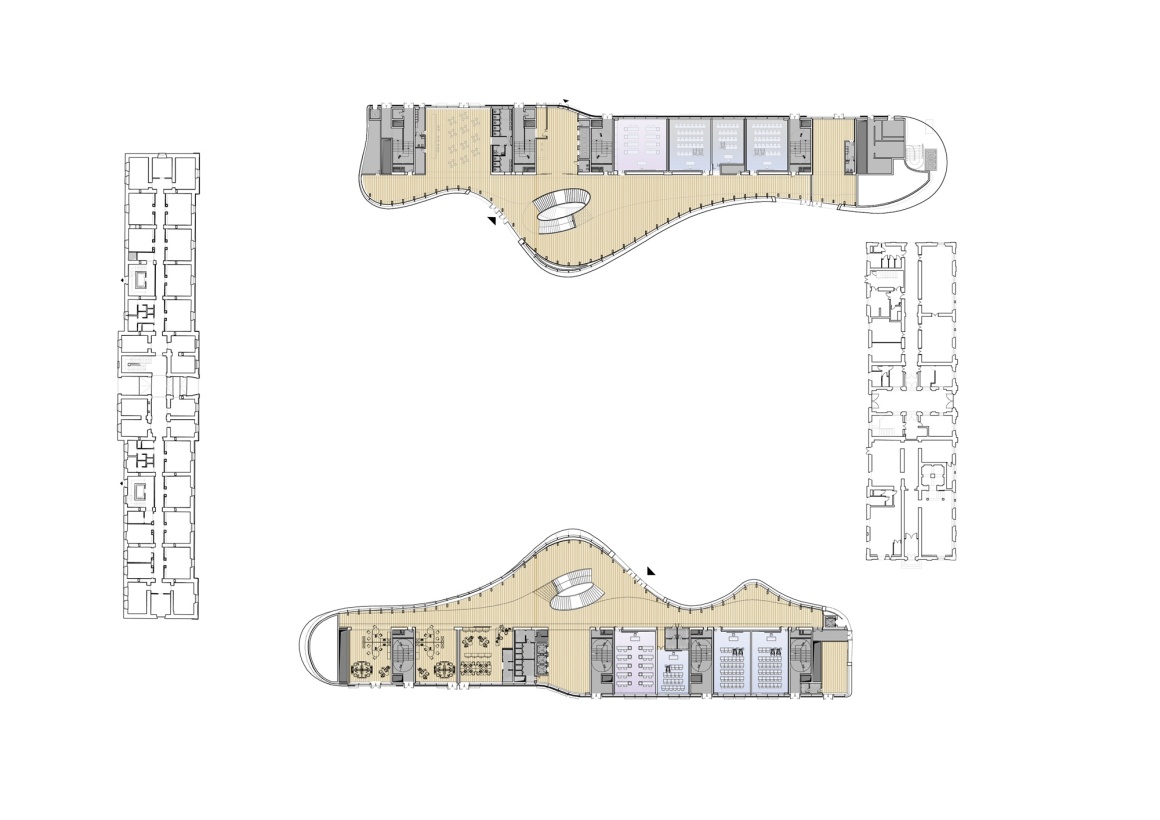
▼首层平面图 The groundlevel
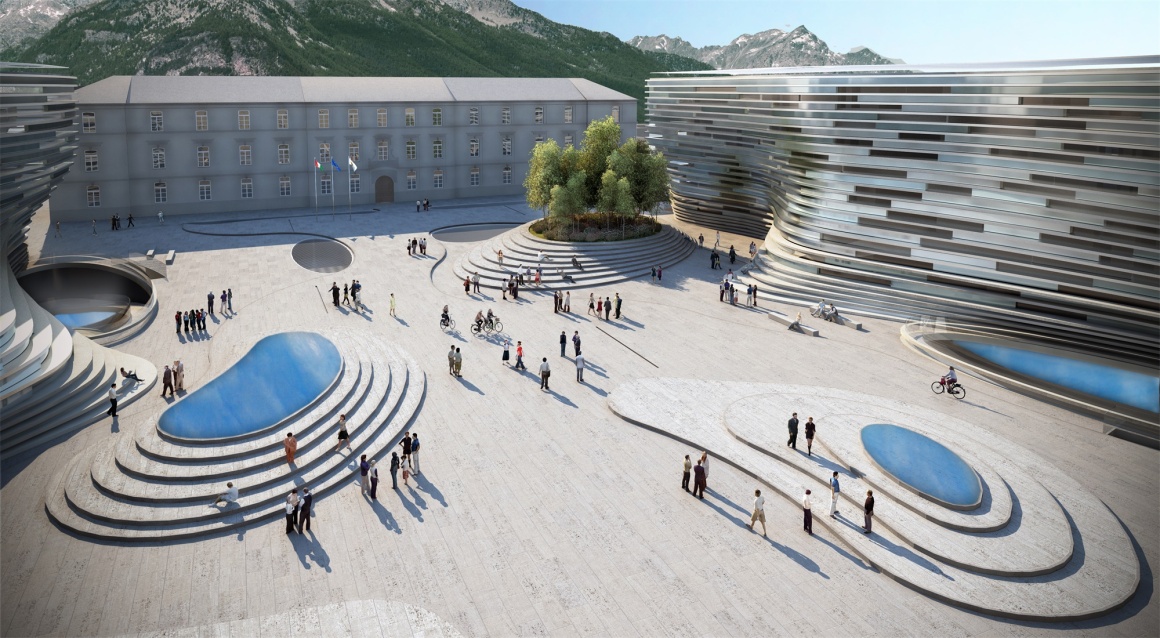
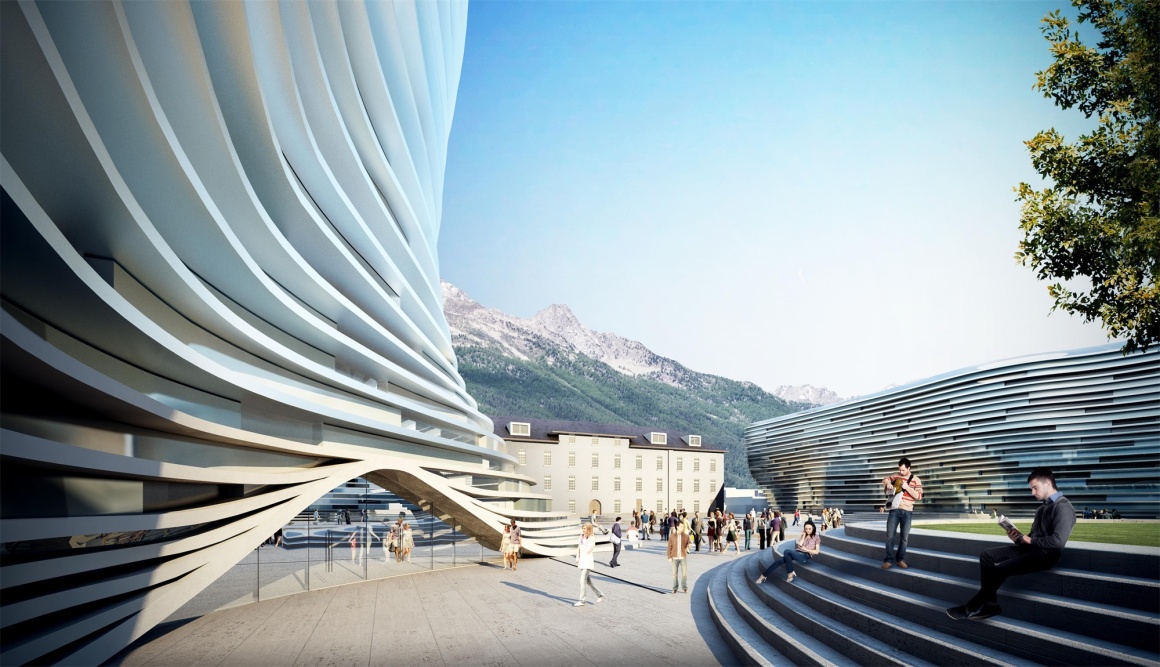
新校区的冰山概念摆脱了原有军营建筑的僵硬感,既有对历史建筑的尊重,又有助于城市记忆。同时,设计从植物界的有机关系中汲取智慧,校园建筑在保持相对独立的基础上又互相关联,与环境和城市融为一体。校园规划在尊重原来平面布局的基础上,彻底改变了整体分布,进行有机的规划。设计鼓励双向交流及互动,大量的公共空间以灵活有效的方式面向城市开放,在便于学院的教学活动的同时满足城市公共功能需求,带来社会附加值。
具体而言,通过对校园活动的私密性进行分级,分层级地对城市开放。将校园广场向城市打开,作为社会活动与学校活动的缓冲空间,消解了内与外的边界性,使得校园与城市进行互动。其他的公共设施比如,运动场馆,会议中心等公共建筑和空间,可用于城市开放性的社会活动。既能提高学校教育设施的利用率,回馈社会,提升城市活力,又能助力建设高品质的综合城市生活。新校区采用前瞻性的智能系统, 以满足校园日后的扩展需求。令学生事务及校园设施管理更便捷,令校园生活更以人为本。
The iceberg concept of the new campus gets rid of the rigidity of the original military barracks. It not only respects the historical buildings, but also contributes to the memory of the city. At the same time, the design draws wisdom from the organic relationship of the plant world, and the buildings are connected to each other while remaining relatively independent, integrating with the environment and the city. On the basis of respecting the original layout, the campus planning completely changed the overall distribution and carried out organic planning. The design encourages communication and interaction. A large number of public spaces are opened to the city in a flexible and effective manner, which facilitates the teaching activities of the college while meeting the needs of urban public functions and bringing social added value.
Specifically, by grading the privacy of campus activities, the city is opened hierarchically. The square is opened to the city as a buffer space for social and school activities, dispelling the boundary between inside and outside, allowing the campus to interact with the city. Other public facilities such as sports venues, conference centers and other public buildings and spaces can be used for urban open social activities. It can not only increase the utilization rate of school educational facilities, give back to the society, and enhance the vitality of the city, but also help build a high-quality comprehensive urban life. The new campus adopts a forward-looking intelligent system to meet the future expansion needs of the campus. Make student affairs and campus facility management more convenient, and make campus life more people-oriented.
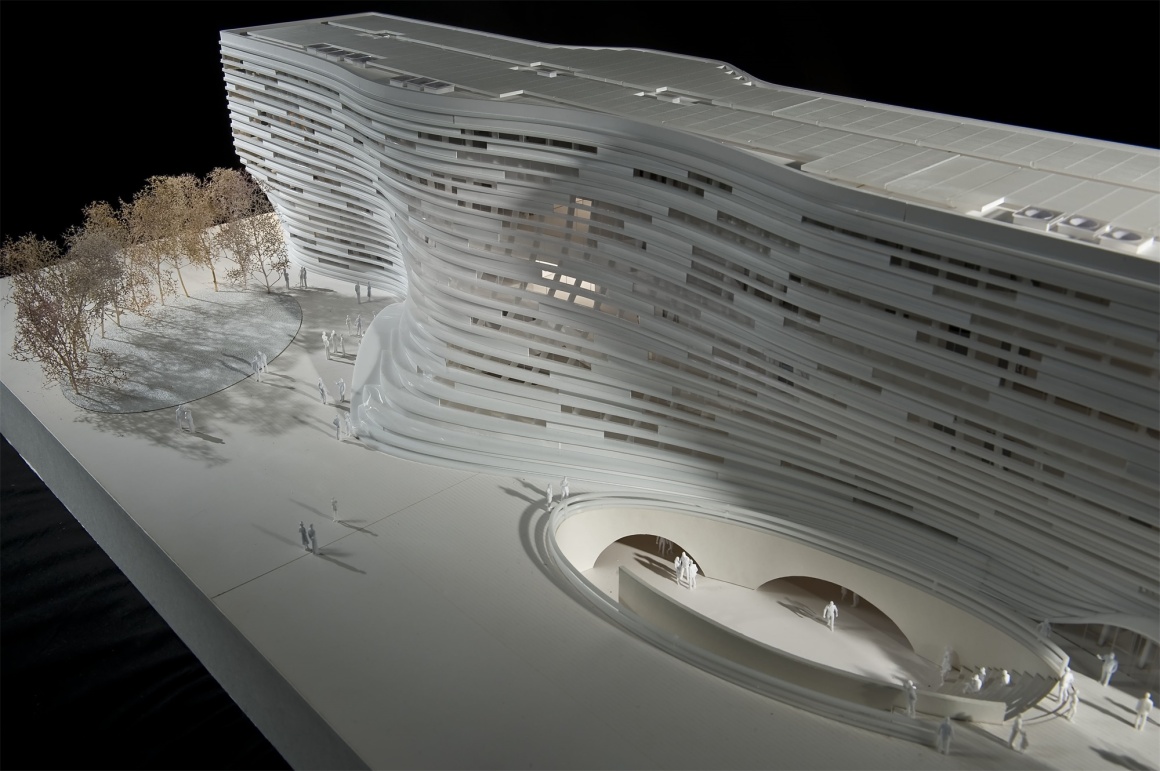
▼建筑模型 Building model
可持续发展校园 Sustainable development of education
瓦莱达奥斯塔大学新校区的规划从可持续角度出发,也是一种对环境和社会效应的回应。开放校园的理念将学校作为城市生活的核心结构,赋予其更多的社会职能,共享资源,形成学校与城市环境间的紧密关系。通过建立改善能源效率、保护资源、提高环境质量的教育社区,实现教育、环境和城市的可持续发展。
The planning of the new campus of the University of Valle d’Aosta is based on a sustainability perspective and is also a response to environmental and social effects. The concept of open campus takes the school as the core structure of urban life, giving it more social functions, sharing resources, and forming a close relationship between the school and the urban environment. Realize the sustainable development of education, the environment, and the city by establishing educational communities that improve energy efficiency, protect resources, and improve environmental quality.
▼能源策略分析图 Environmental strategies
充分研究当地的典型气候条件,包括确定相关区域的潜力和关键点,如太阳路径、阴影变化和盛行风的变化,避免新建筑过于影响周围其他建筑物的日照情况。依据这些条件设计出既符合气候和环境需求又具有审美的外观的体量。使用玻璃外板和不透明板构成立面结构,提供自然采光以及主动遮阳。既保证了舒适的室内环境,又赋予建筑外表可识别的特征。
特别关注优化能源利用效率,针对性地提出最佳解决方案。将可再生能源包括地下水热泵、冷凝锅炉、光伏发电、太阳能热发电,用于多种技术下的混合使用,在保证建筑物低能耗的同时,提高收益/成本比,确保房屋的最佳性能,达到极高的环境质量标准。与传统的天然气加热系统相比,采用可再生能源驱动系统以减少向大气排放污染物和温室气体排放。
Fully study of the local typical climatic conditions, including determining the potential and key points of the relevant area, such as the sun’s path, changes in shadows, and changes in prevailing winds, so as to avoid new buildings from overly affecting the sunlight conditions of other surrounding buildings. Based on these conditions, a volume that not only meets climate and environmental requirements but also has an aesthetic appearance is designed. Use glass outer panels and opaque panels to form the facade structure to provide natural lighting and active shading. It not only ensures a comfortable indoor environment, but also gives the building exterior recognizable characteristics.
Special attention is paid to optimizing energy efficiency, and the best solutions are proposed. Renewable energy including groundwater heat pumps, condensing boilers, photovoltaic power generation, and solar thermal power generation are used for mixed use under a variety of technologies. While ensuring low energy consumption in buildings, it increases the revenue/cost ratio and ensures the best performance of the architecture to get the extremely high environmental quality standards. Compared with traditional natural gas heating systems, renewable energy drive systems are used to reduce emissions of pollutants and greenhouse gases to the atmosphere.
▼气候分析与能源表现 Energetic performance
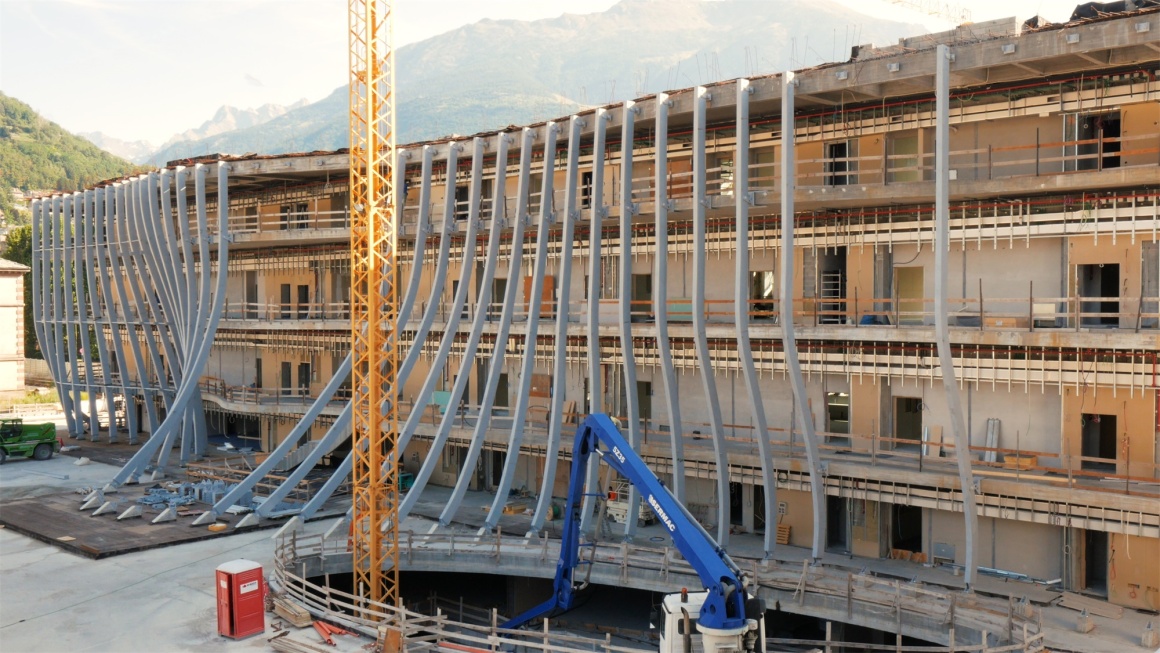
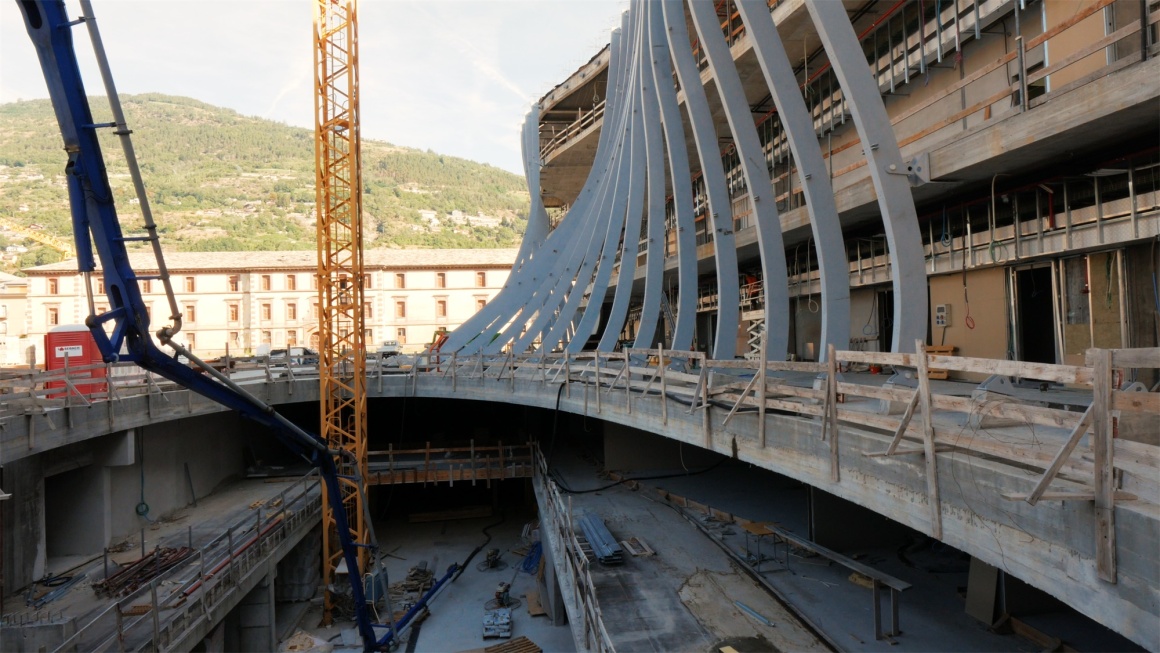
回收雨水并将其积聚在专用的地下储罐中,用于清洁用水和灌溉绿地。并且为了减少浪费,还将实施高效的绿地灌溉系统。项目从施工阶段,就采取适当措施以减轻施工现场扬尘的扩散。
Recover rainwater and accumulate it in dedicated underground storage tanks for cleaning water and irrigating green spaces. And in order to reduce waste, an efficient green irrigation system will be implemented. From the construction stage of the project, appropriate measures have been taken to reduce the spread of dust on the construction site.
▼施工现场 Construction
▼施工现场视频 Construction video
目前,瓦莱达奥斯塔大学新校区正在紧张的施工建设中。从理念到实践,该项目的设计和建设采取众多节能措施、制定与城市共生的开放性策略。通过建筑的力量为环境发声;用设计的语言搭建历史与现代的平衡;以地域气候、人本主义理念为可持续发展的核心。作为意大利首批零耗能建筑,也必将成为创造奥斯塔市新文化魅力的催化剂。
Currently, the new campus of the University of Valle d’Aosta is under intense construction. From concept to practice, the design and construction of the project adopted numerous energy-saving measures and developed open strategies for symbiosis with the city. Make a sound for the environment through the power of architecture; use the language of design to build a balance between history and modernity; take regional climate and humanistic ideas as the core of sustainable development. As the first batch of zero-energy buildings in Italy, it will also become a catalyst to create the new cultural charm of Aosta.
位置:意大利,奥斯塔
类型:委托设计
时间:2011年 – 正在建设中
项目方:NUV – Nuova Università Valle Valdostana
建筑设计及项目管理:MC A 建筑事务所和 Pession Studio Associato
MC A 团队:MC A Mario Cucinella, Giulio Desiderio, Michele Olivieri, Julissa Gutarra, Nada Balestri, David Hirsh, Rigoberto Arambula, Fabrizio Bonatti, Luca Stramigioli, Davide Stolfi; Giulia Pentella, Alberto Bruno; Yuri Costantini;
结构工程:Sintecna
建筑服务工程:Golder Associates – Metec & Saggese – Energy Services
声学工程:Onleco
消防设计:GAE Engineering
视觉效果:Engram Studio
艺术指导:MC A, Giulio Desiderio, Davide Stolfi
Location:Aosta, Italy
Type:Commission
Time:2011 – now
Client:NUV – Nuova Università Valdostana
Project:Mario Cucinella Architects and Pession Studio Associato
Team MC A :MC A Mario Cucinella, Giulio Desiderio, Michele Olivieri, Julissa Gutarra, Nada Balestri, David Hirsh, Rigoberto Arambula, Fabrizio Bonatti, Luca Stramigioli, Davide Stolfi; Giulia Pentella, Alberto Bruno; Yuri Costantini;
Structure Engineering:Sintecna
Building Services Engineering:Golder Associates – Metec & Saggese – Energy Services
Acoustic Engineering:Onleco
Fire and Safety Design:GAE Engineering
Visual:Engram Studio
Artistic Supervision:MC A, Giulio Desiderio, Davide Stolfi
更多read more about: MC A 建筑事务所













0 Comments