本文由 魏玛景观 授权mooool发表,欢迎转发,禁止以mooool编辑版本转载。
Thanks Weimar Group for authorizing the publication of the project on mooool, Text description provided by Weimar Group.
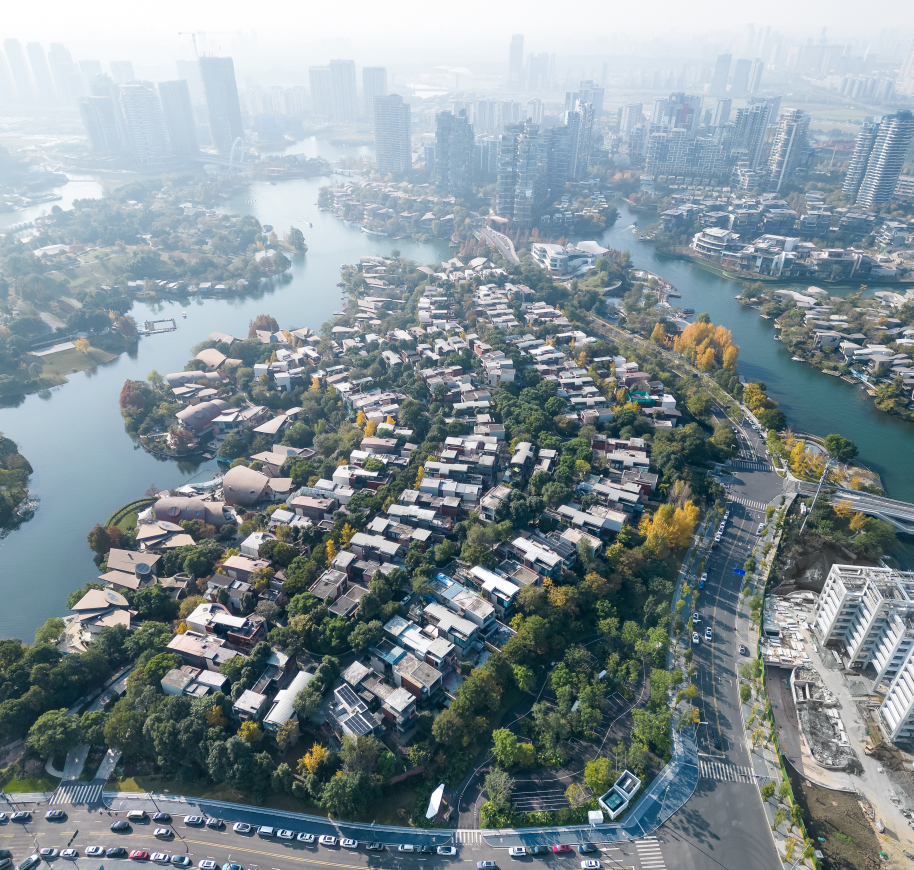
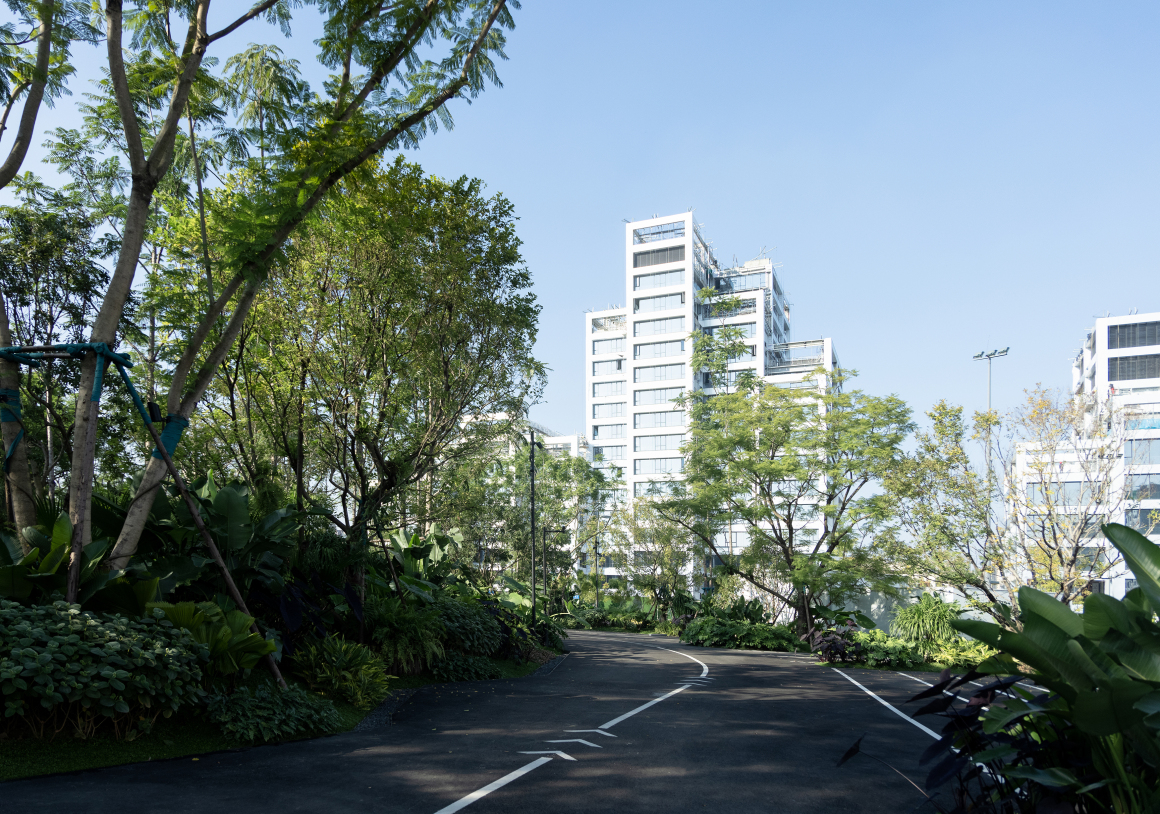
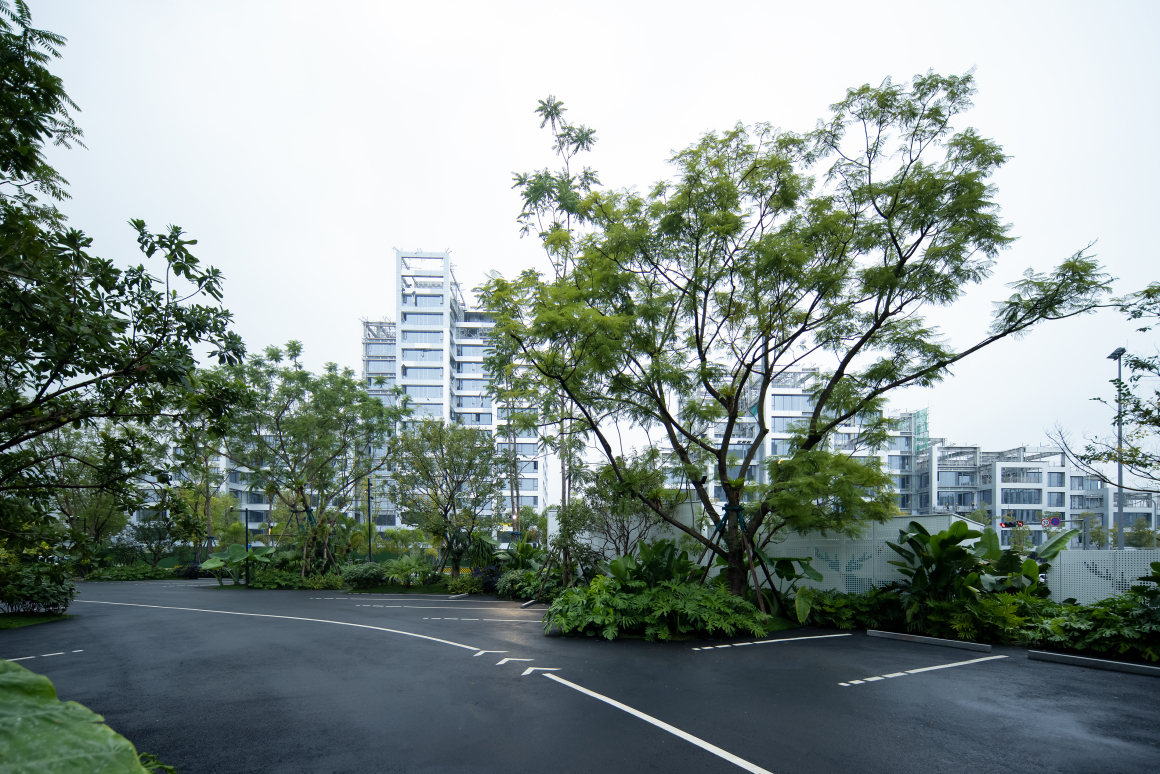
魏玛景观:项目所在地,位于未来10年麓湖商业板块的核心区,场地对面两侧分别为A7、A3两大商业空间,与热门非标商业CPI仅一桥之隔。设计之初,预见了未来该区域即将激增的人车流量,意在缓解后续场地拥挤无绿地空间的问题。
Weimar Group: The project is located in the core area of Luhu commercial plate in the next 10 years. There are two commercial Spaces on the opposite sides of the site, A7 and A3, which are only one bridge away from the popular non-standard commercial CPI. At the beginning of the design, it anticipated the future surge of people and vehicles in the area, and was intended to alleviate the problem of crowded and no green space in the future.
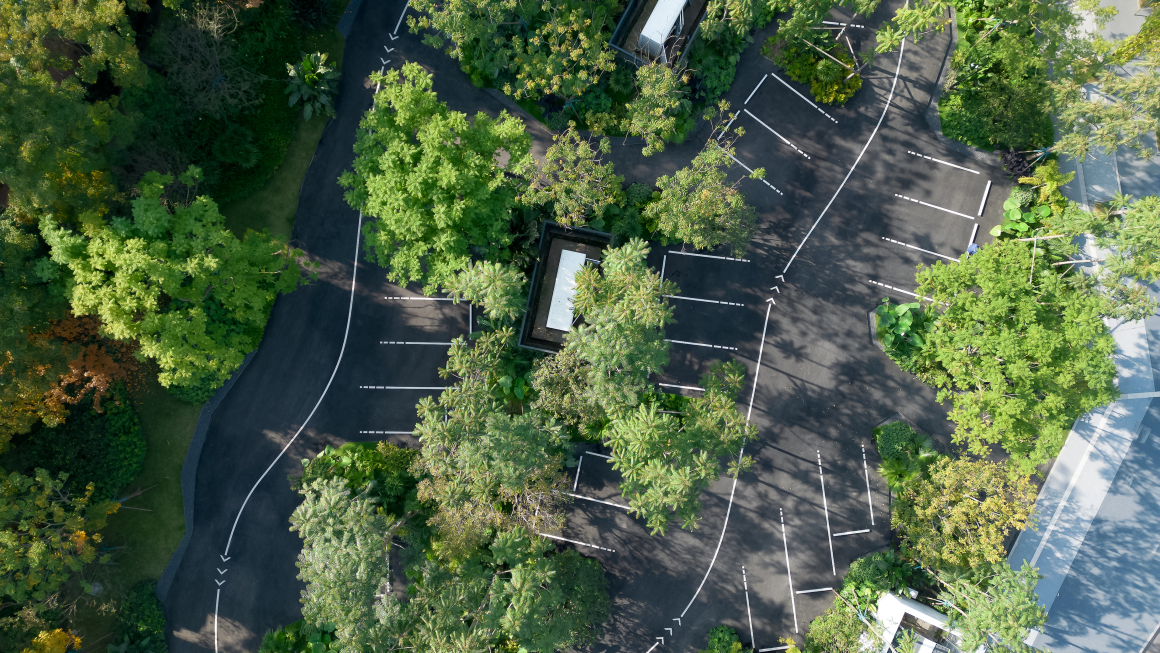
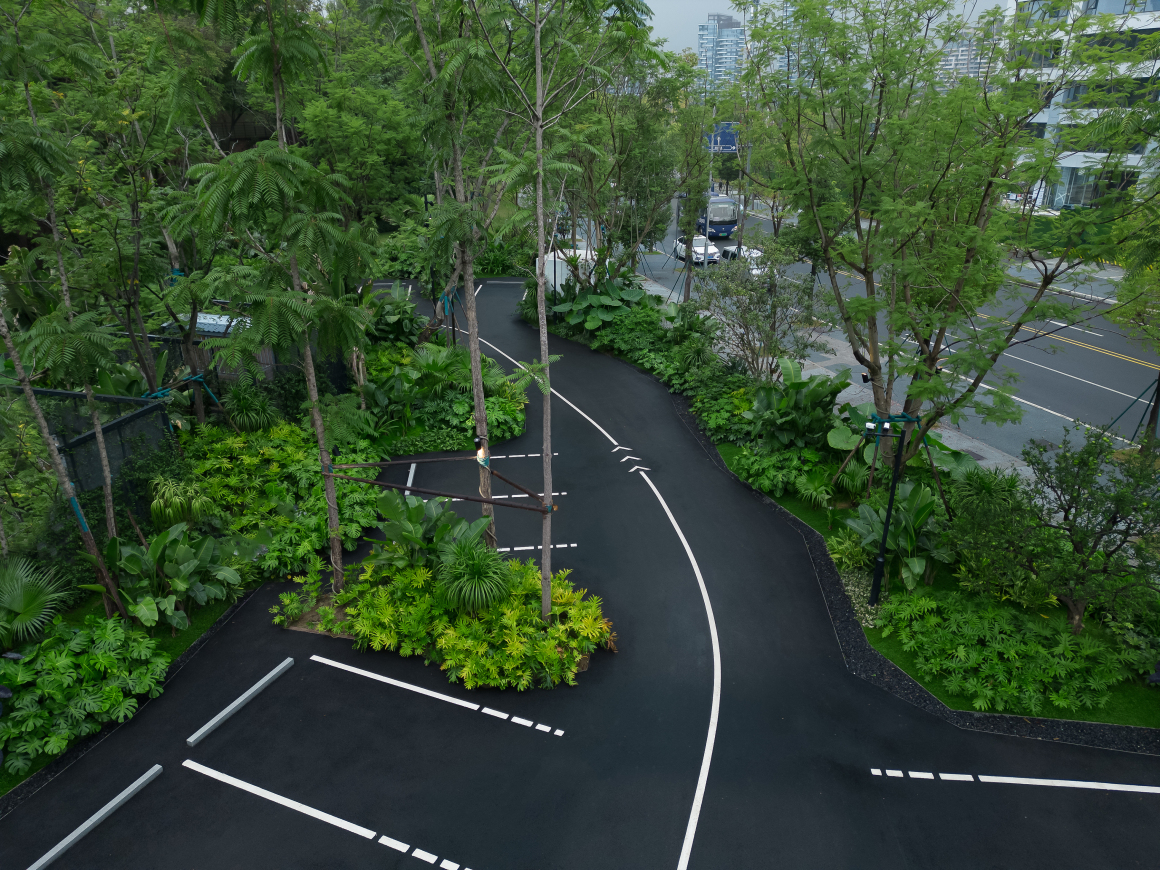
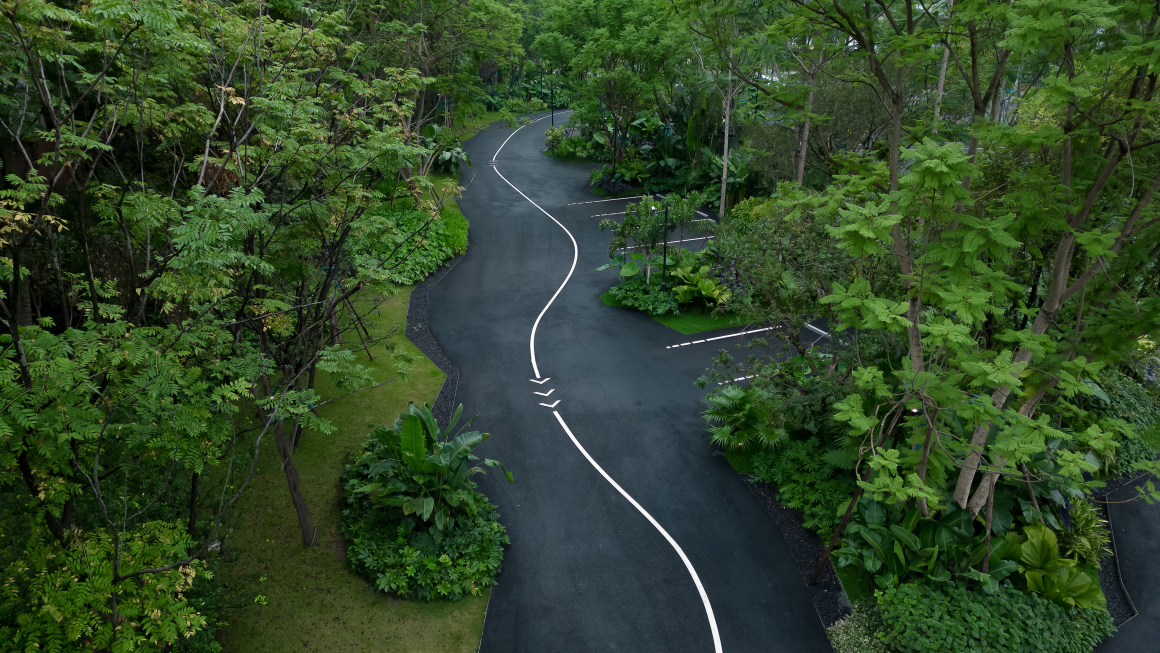
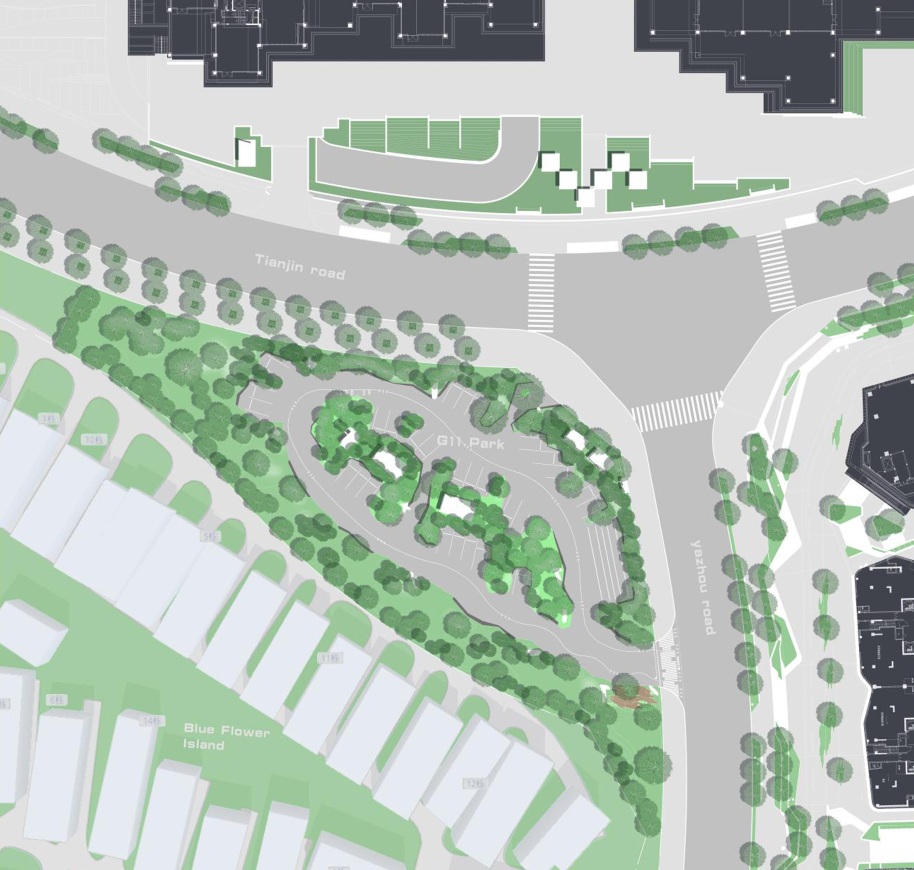
▽项目总览和项目平面图
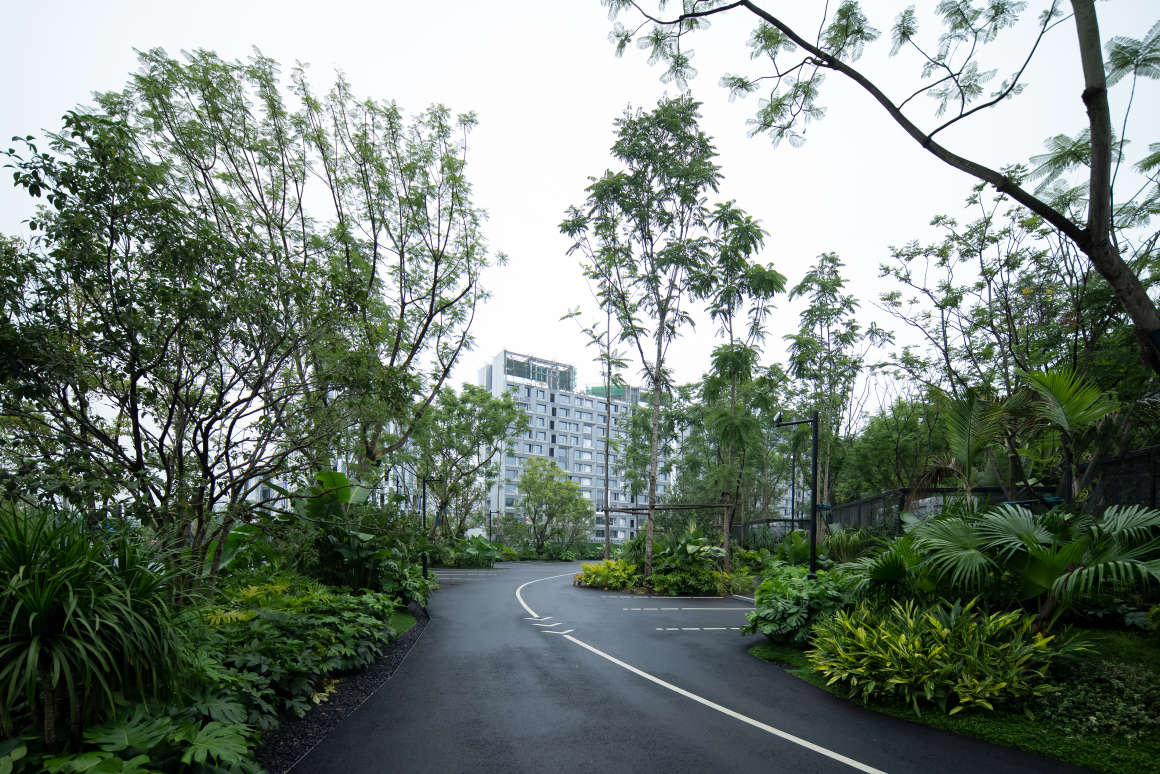
整个“麓湖社区”,是成都市公园城市先行重点社区(成都市第二批近零碳试点社区),除承载公共交通系统和基础设施改善交通便利性之外,公园与城市空间的有机渗透与融合,将是我们对于这个小小场地赋予更多的可能性的开始。我们带着探索城市公园低碳运维的维度对场地形进行了思考——城市绿地如何成为城市多功能绿色公共空间?
The whole “Luhu Community” is the first key community of Chengdu Park City (the second batch of near zero carbon pilot communities in Chengdu). In addition to carrying public transportation system and infrastructure to improve transportation convenience, the organic penetration and integration of park and urban space will be the beginning of giving more possibilities to this small site. With the dimension of exploring low-carbon operation and maintenance of urban parks, we think about the field topography — how can urban green space become a multi-functional green public space?
▽板桁架
ONE PARK 实验场地
ONE PARK TEST SITE
Park这个单词,就承载了场域的一切可能,麓湖作为公园城市的示范区社区一直在坚持对“生态、可持续、环保”理念上的实践与探索,拥有多个相对独立的主题“生态实践”,我们也想在此完成一次人工与自然的迭代试验——低影响开发LID(Low-Impact Development)的可循环的生态空间。
LID在海绵城市中的技术体现:雨水花园:通过种植植物和设置蓄水设施,收集和储存雨水,用于景观灌溉或地下水补给。生态滞留草沟:利用草沟收集和过滤雨水,降低洪峰流量。绿色街道:使用透水铺装材料,增加渗水能力,减少径流。可渗透路面:采用特殊材料铺设路面,增加雨水下渗。生态屋顶:通过绿色屋顶收集雨水,减少屋顶径流。雨水再生系统:收集、处理和再利用雨水,用于灌溉或其他。
The word Park carries all the possibilities of the field. park is a park and a parking lot.As a demonstration area community of Park City, Luhu has been adhering to the practice and exploration of the concept of “ecology, sustainability and environmental protection”, and has several relatively independent themes of “ecological practice”. We also want to complete an iterative experiment of artificial and nature here — LID (Low-Impact Development) recyclable ecological parking lot.
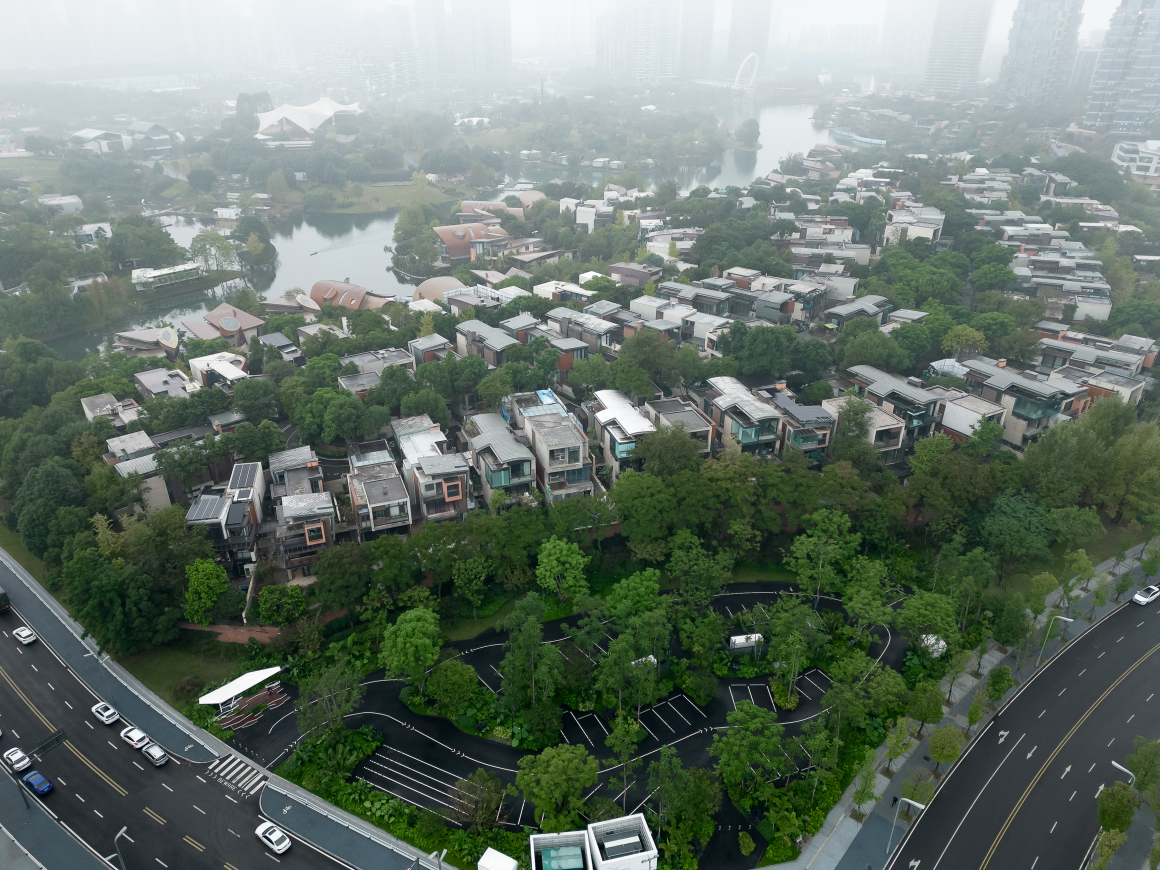
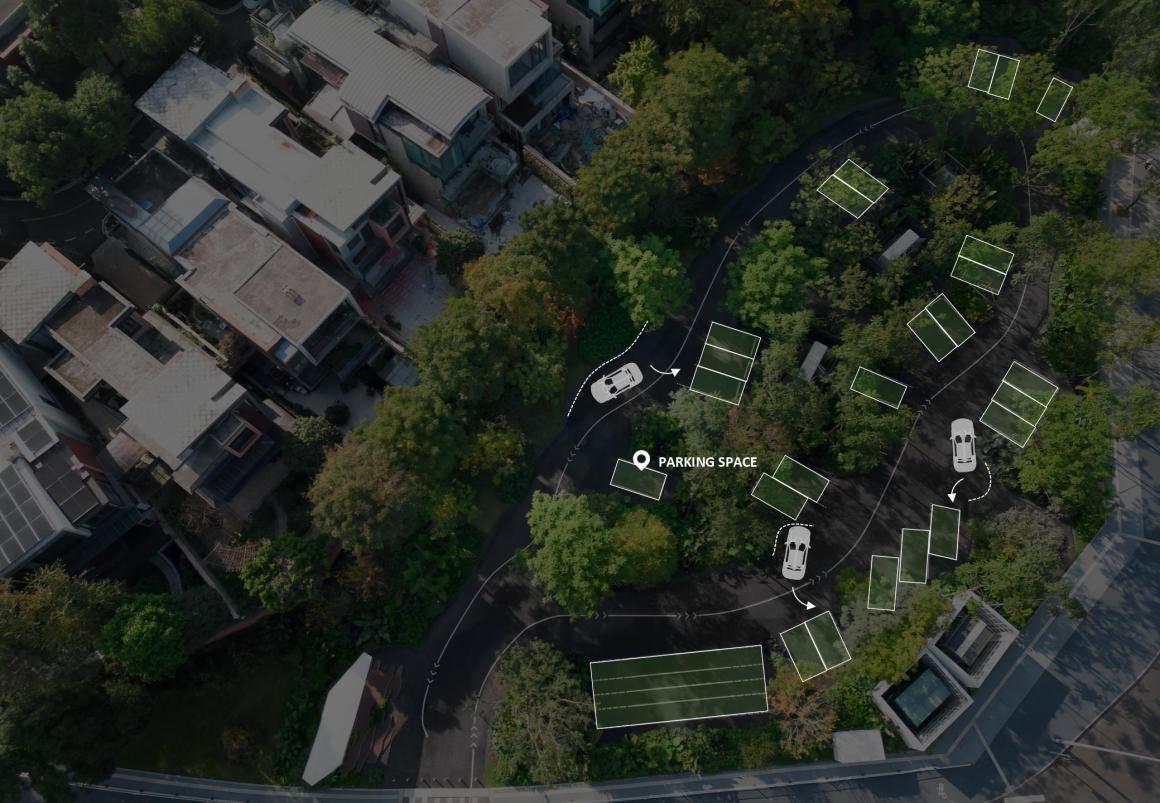
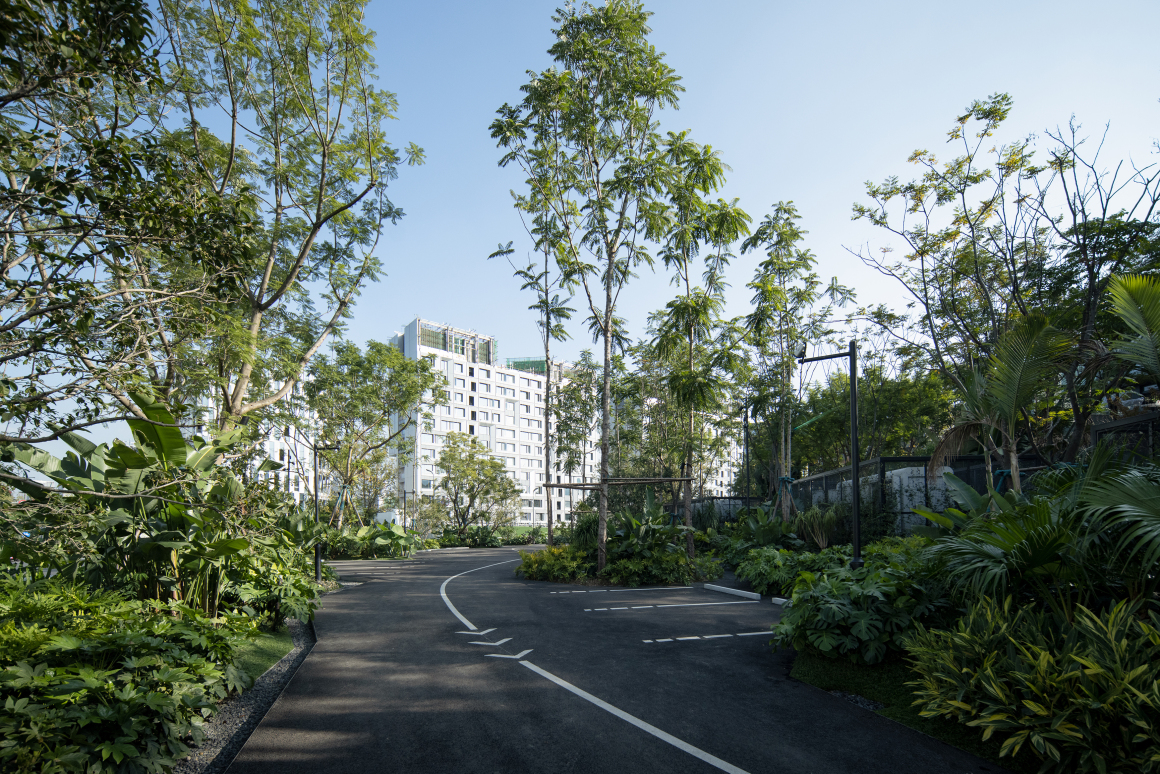
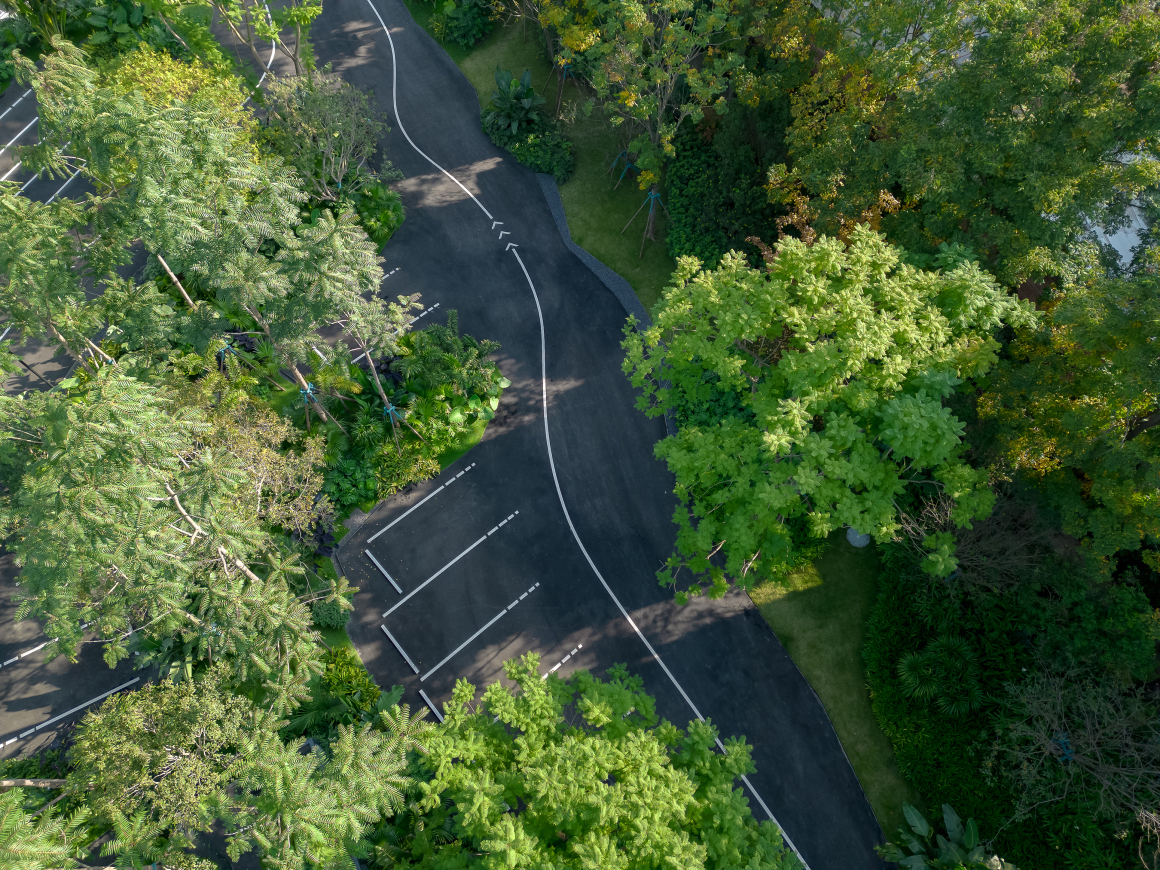
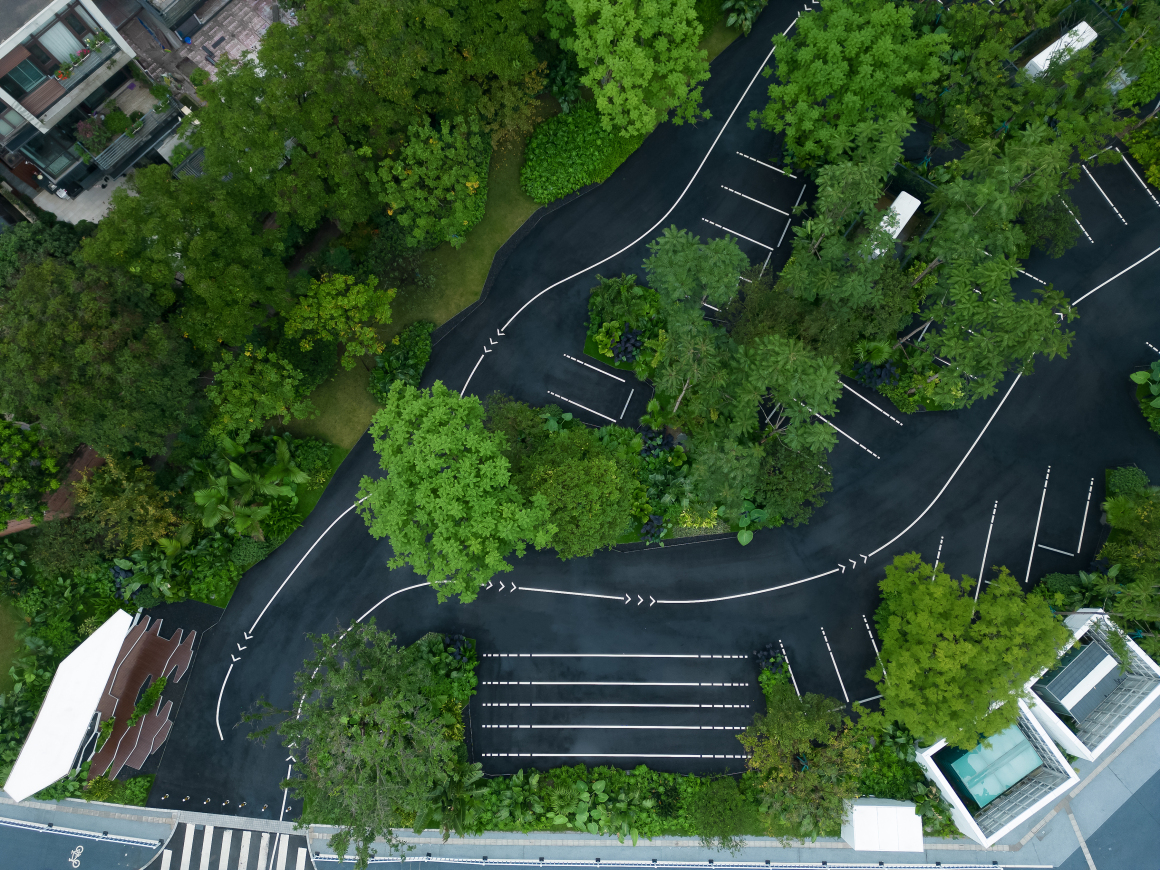
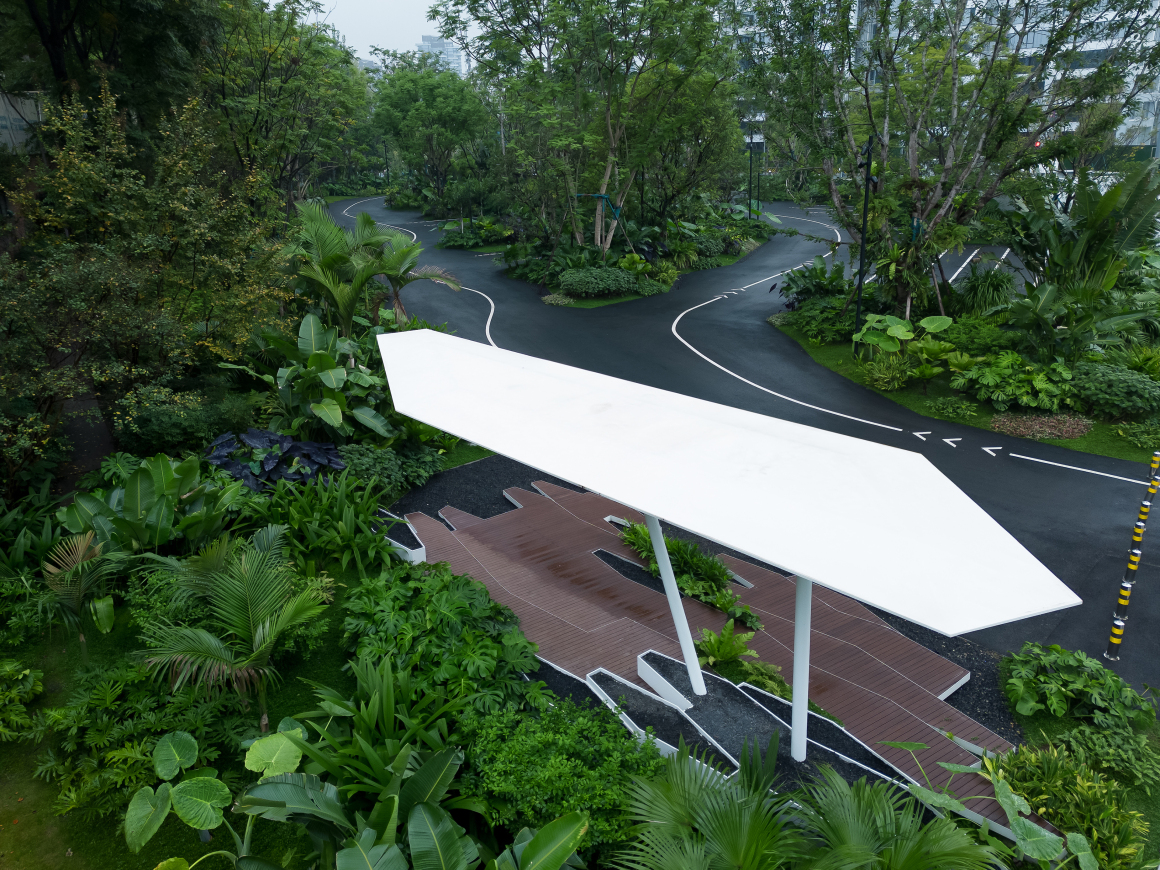
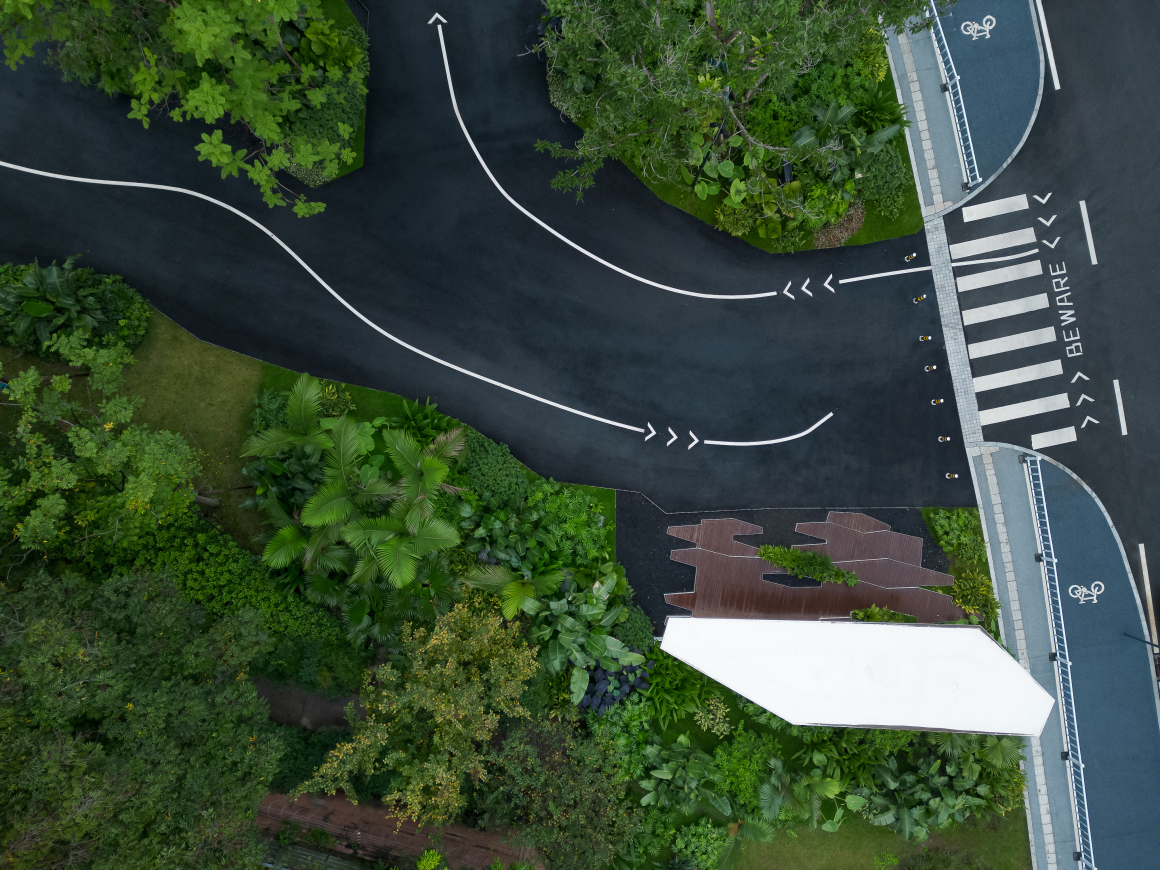
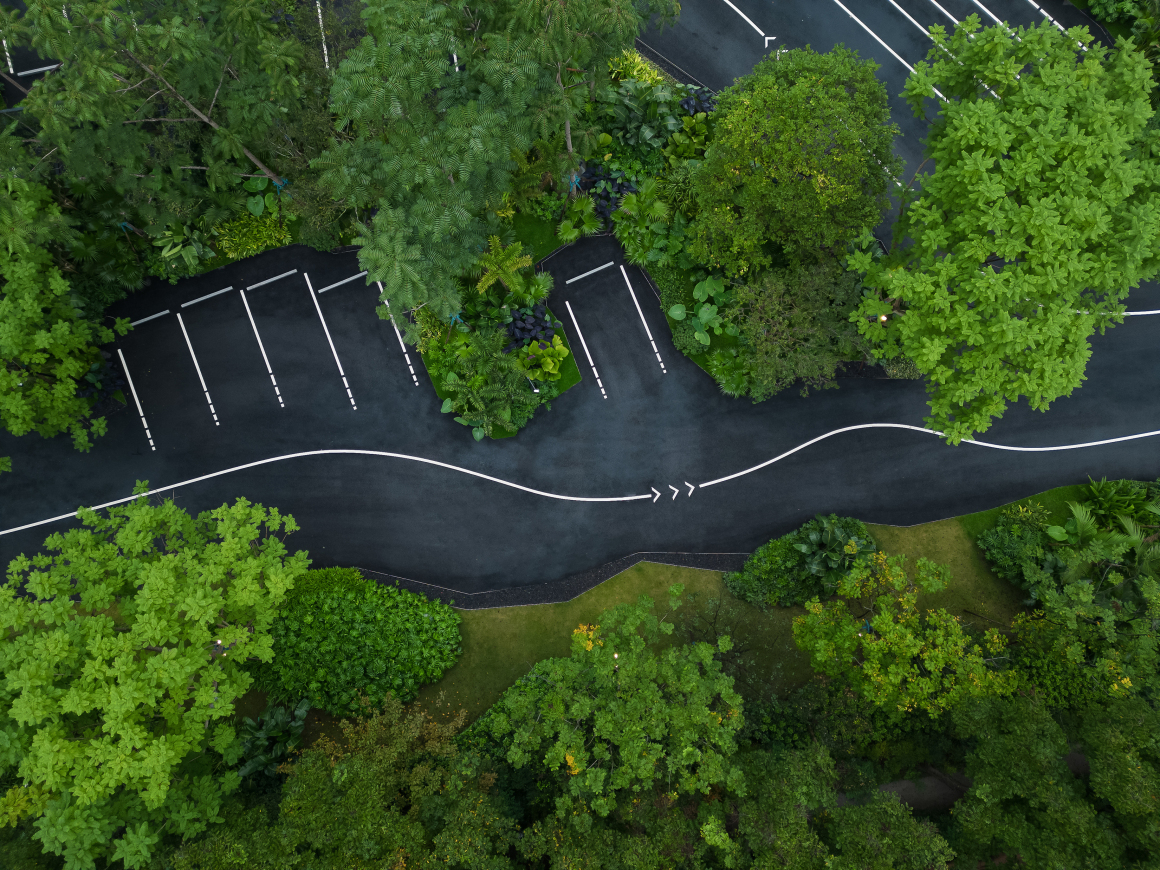
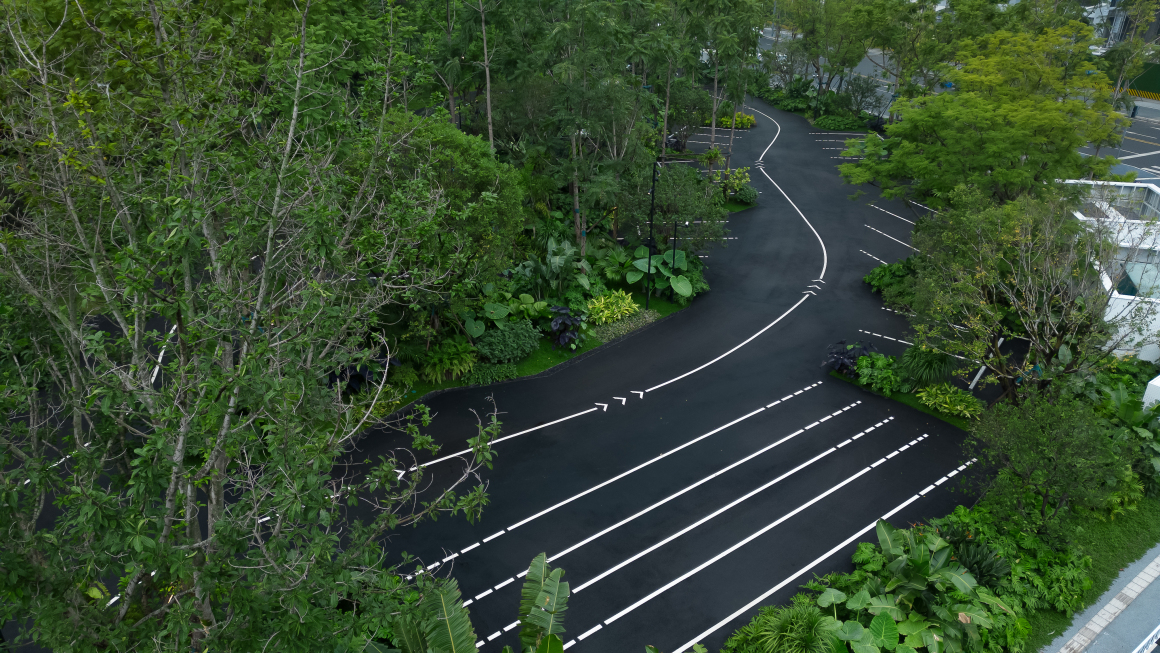
▽项目鸟瞰和停车空间分析
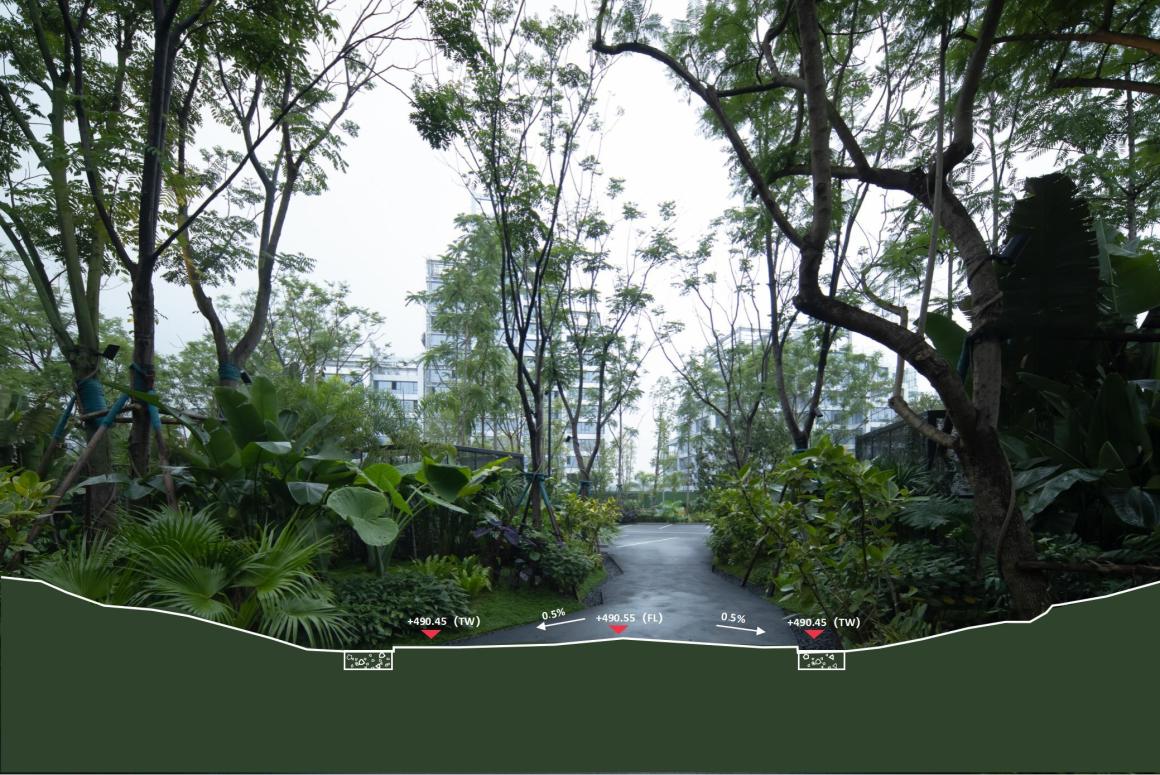
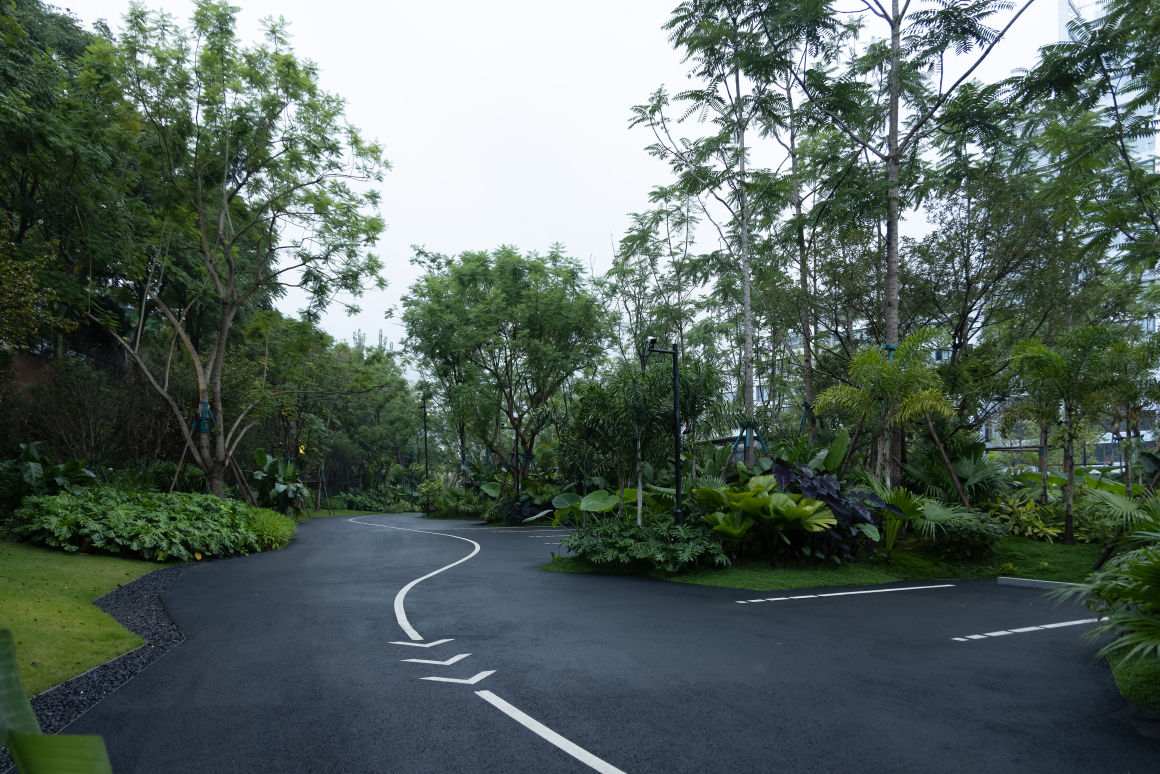
▽停车空间人行视角
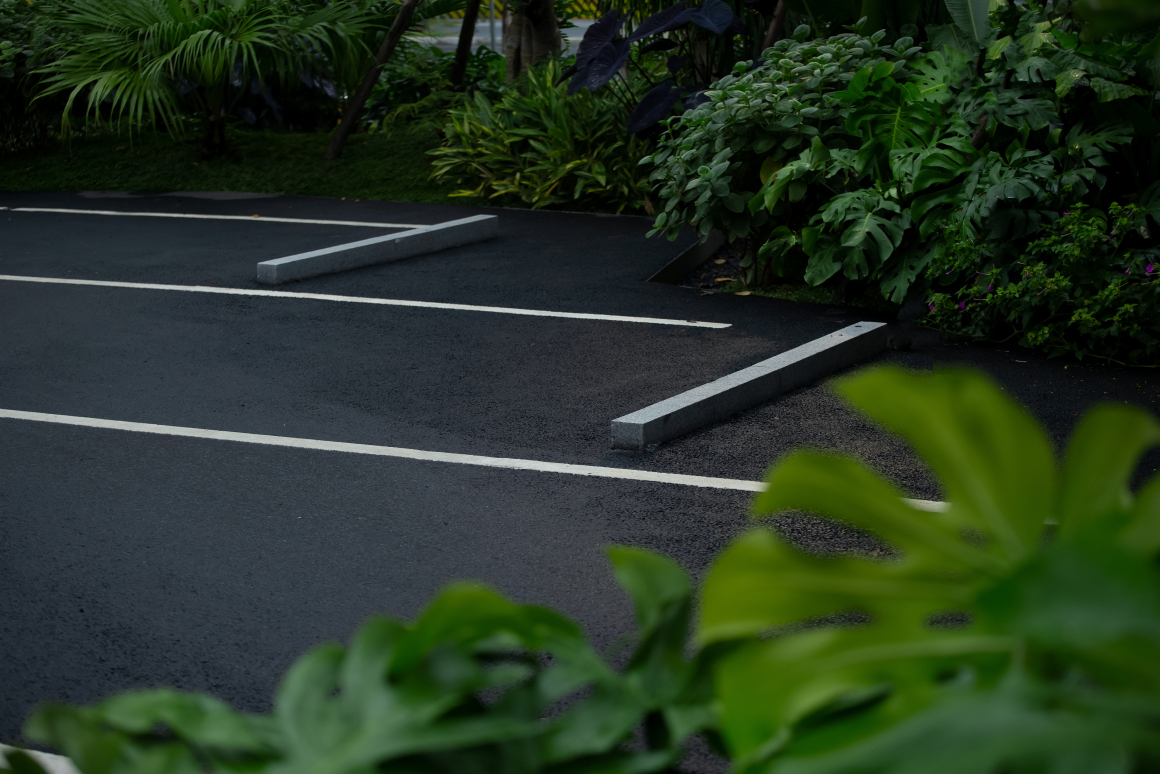
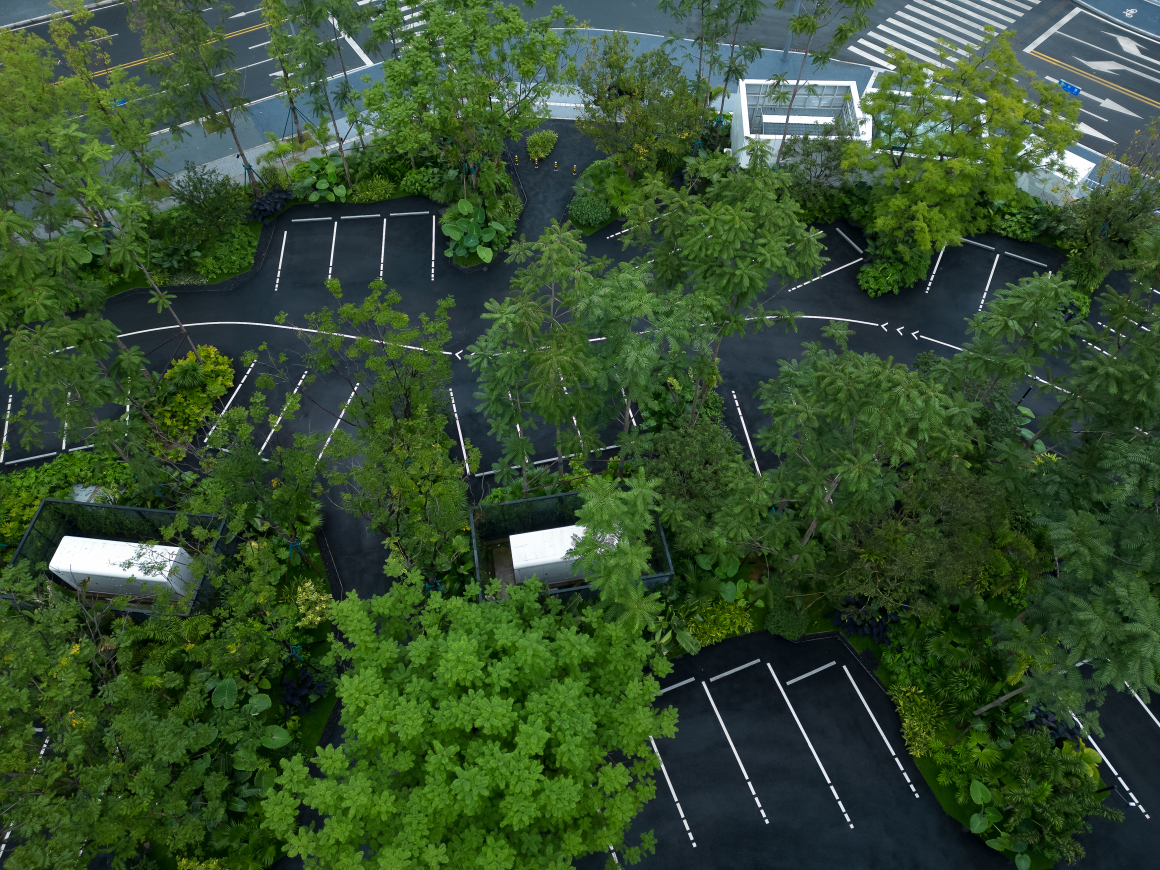
▽停车空间局部鸟瞰
整体设计理念
OVERALL DESIGN CONCEPT
从项目之初到呈现,我们根据麓湖整体的规划和定位,保证周边环境不被破坏且不影响停车噪音对北侧居民的影响。我们的设计目标也包括:1)满足客户对未来场地的使用需求;2)北侧现状原生树进行保留,并注意通过设计减少汽车噪音、尾气对北侧居民的影响;3)对于植物的设计进行多元尝试,作为未来A7项目的样板实验场地;4)满足公园城市下的设计规范,将生态可持续的理念融于场地内。
1) To meet customers’ needs for future site use;2) The existing native trees on the north side should be retained, and attention should be paid to reducing the impact of vehicle noise and exhaust on the residents on the north side through design;3) Make multiple attempts on the design of plants as a sample test site for the future A7 project;4) Meet the design specifications under the Park City and integrate the concept of ecological sustainability into the site.
我们的解决策略
OUR SOLUTION
在怠速情况下,车内一氧化碳浓度迅速上升。当车速为0km/h时,一氧化碳浓度在20分钟左右开始超过国家标准限值(50ppm),并且随着时间的推移浓度不断升高。当车速为10km/h时,一氧化碳浓度在约30分钟左右开始超标。而当车速为20km/h时,一氧化碳浓度在约40分钟左右开始超标。
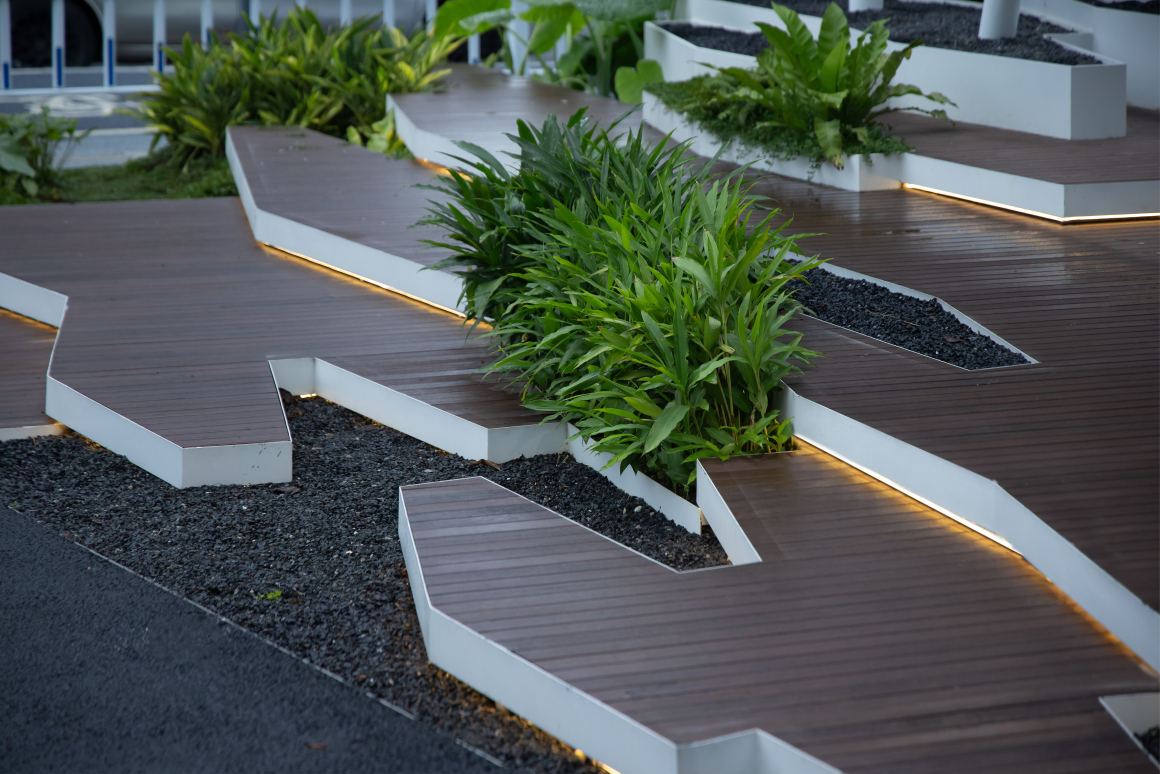
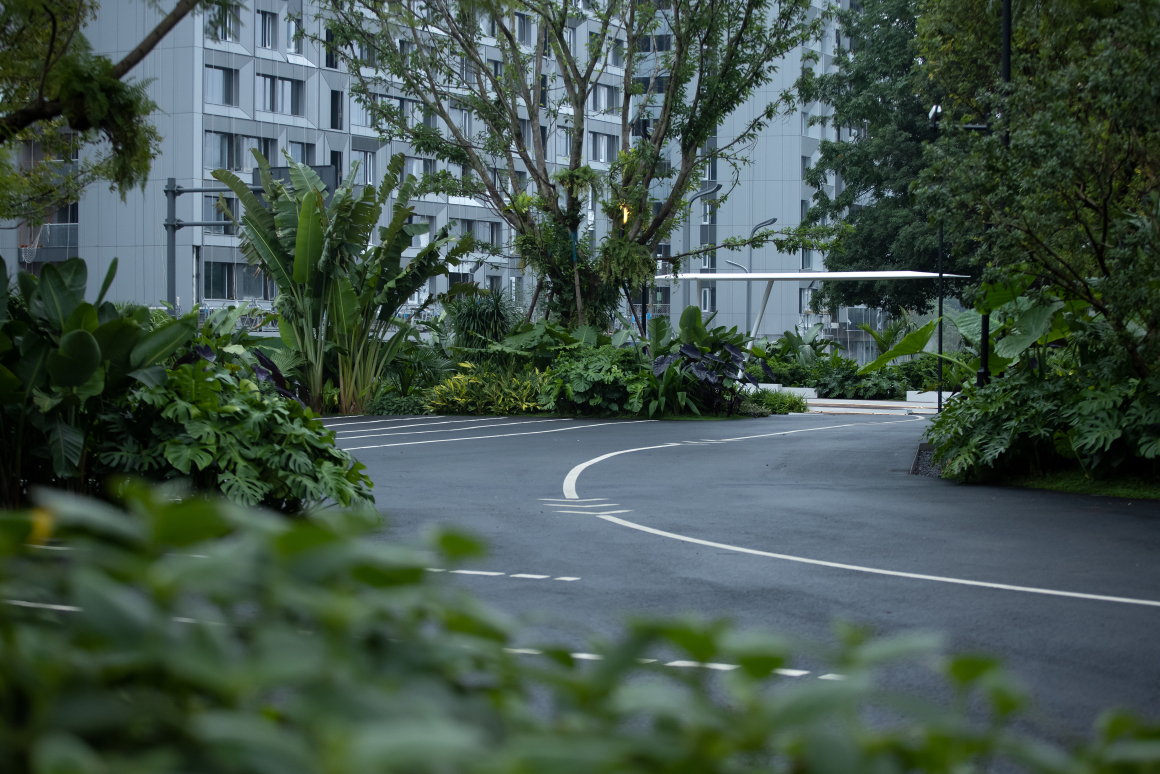
项目面积5220平方米,绿化面积为3080平方米,基于树的光合作用速率,每平方米树每天可以释放氧气1.25千克 ,可以吸收二氧化碳1.6千克。故场地内一天可以产生氧气总量为:3080平方米*1.25千克=3850千克利用植物模糊边界,将规范融于场地。道路两侧设置300mm-500mm不等砾石带,让雨水回流绿地,调节地面温度的同时达到绿化灌溉目。暴雨时,路面多余的水溢出,流入到达排水的目的。
Using plants to blur the boundary, the norms are integrated into the site. Gravel belts ranging from 300mm-500mm are set on both sides of the road to allow rainwater to return to the green space, adjust the ground temperature and achieve green irrigation. During the rainstorm, the excess water on the road overflows and flows into the water for the purpose of drainage.
▽数据阐述
▽雨水渗透示意图
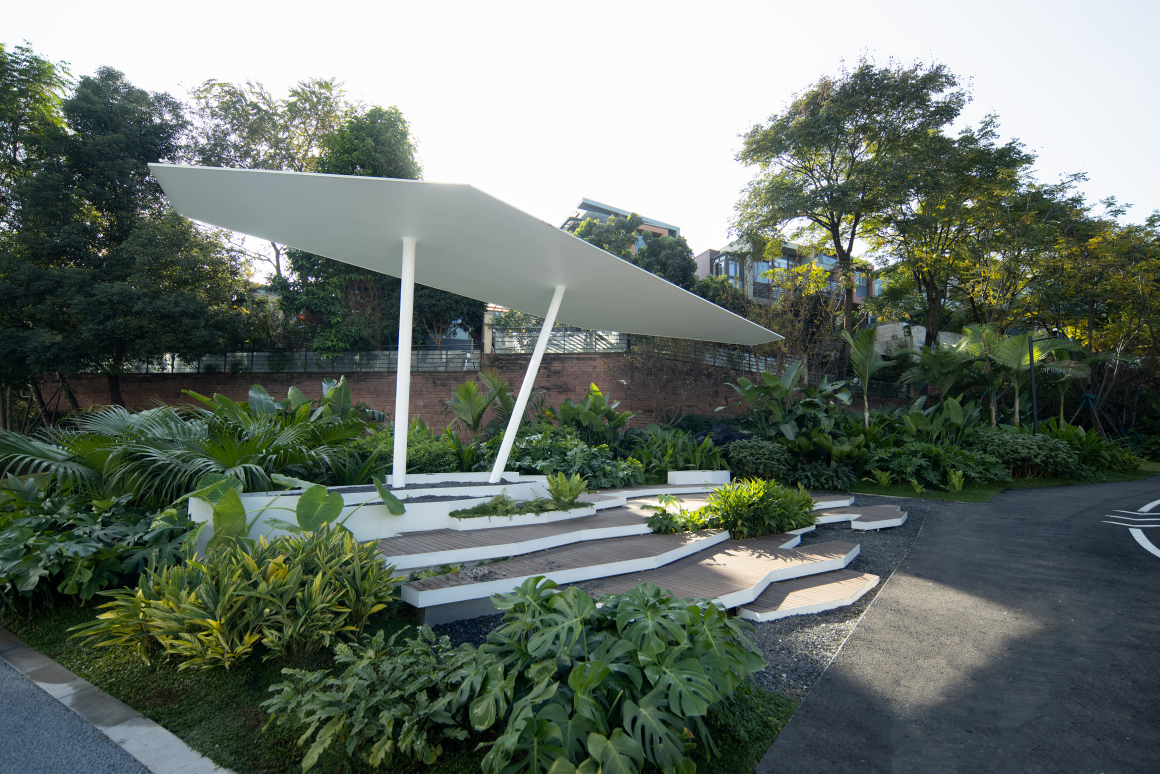
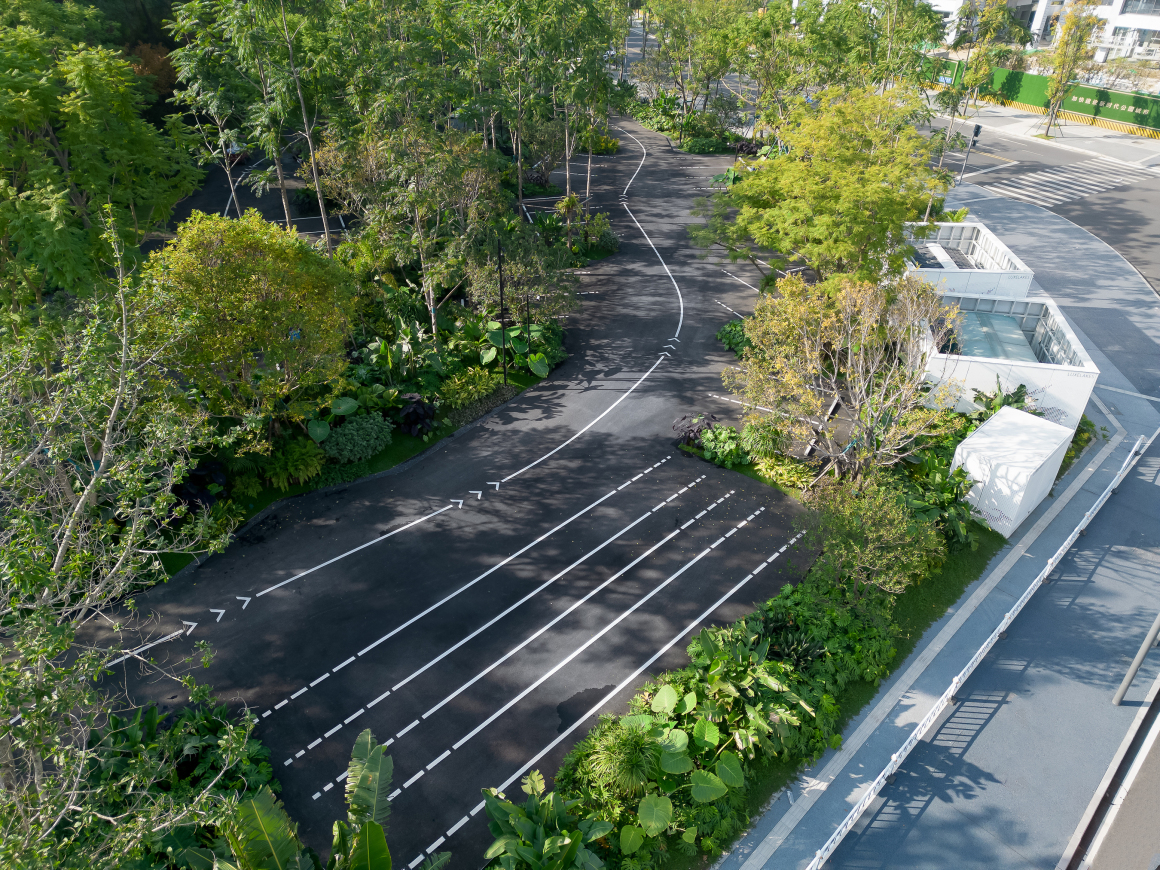
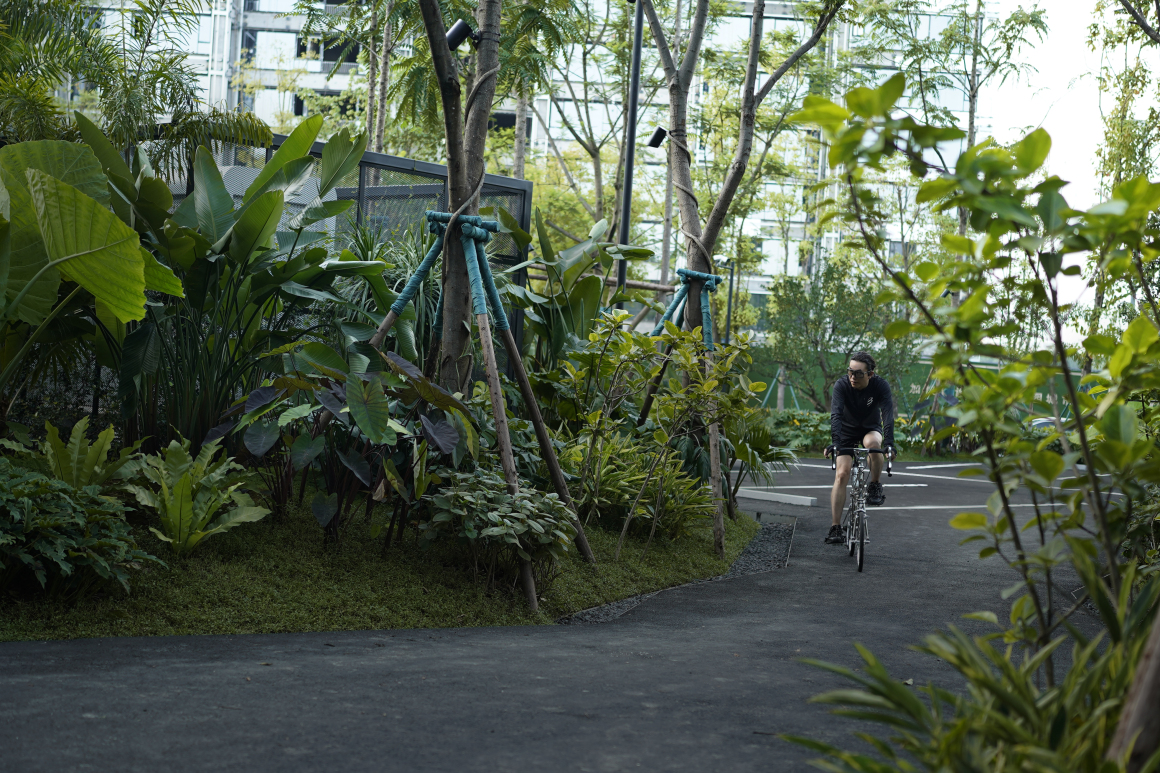
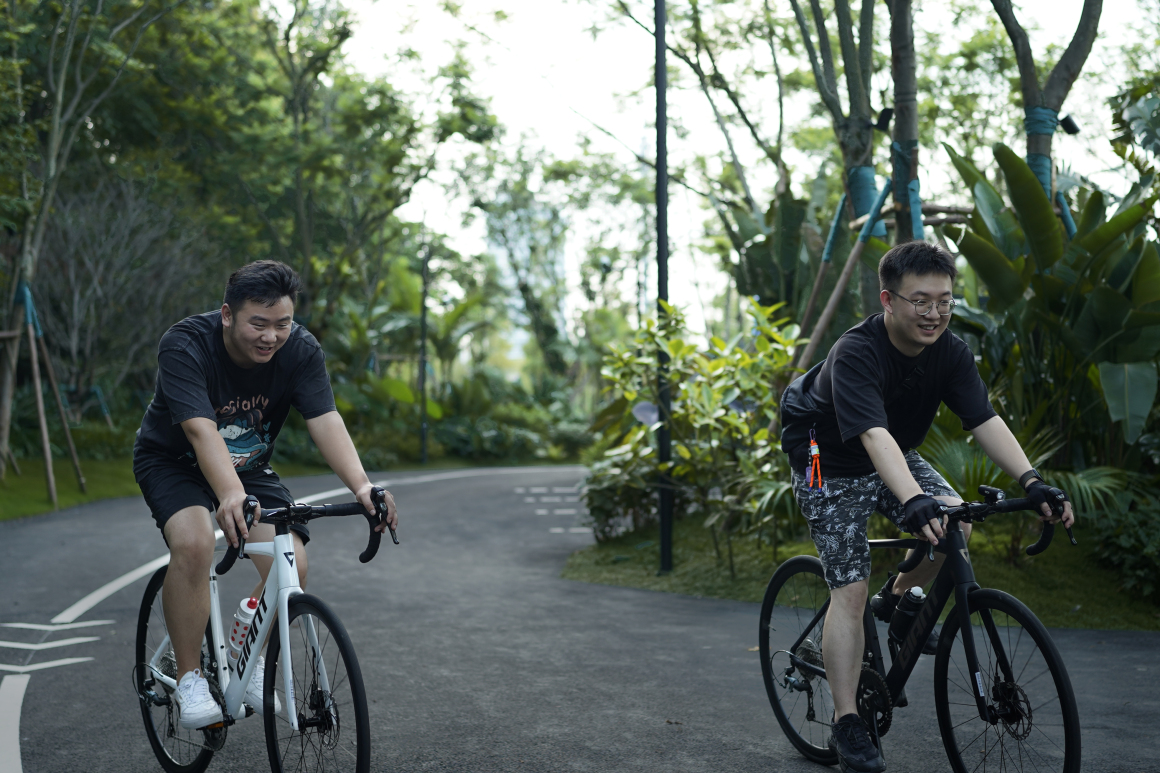
设置车行、人行出入口,人车分流。车行进过程中,局部扩大道路宽度,方便停车与错车。考虑后续规划该区域为麓湖生态城Mini bus接驳点之一,入口处用轻盈的板桁架,代替传统停车入口的安保亭,便于管控的同时,也兼具后续整体景区使用。
Set up car, pedestrian entrance, people and vehicles. In the process of driving, the road width is partially enlarged to facilitate parking and wrong vehicles. This area is considered to be one of the Mini bus connection points of Luhu Eco-City in the future planning. Light plate truss is used at the entrance to replace the security pavilion at the traditional parking entrance, which is convenient for management and control, and can also be used in the overall scenic area in the future.
靠近居住区一侧保留场地原生树种的同时,并将绿化带厚度设置到11米,最大限度降低污染和噪音。植物运用在四川乡野常见但鲜用的植物椿树,乔灌木搭建竖向空间,利用形成生态可续的「小岛绿肺」。基于植物的光合作用,场地内一天能产生3850千克氧气,汽车碳排放一天为179.8千克。创造生态小气候,降低汽车尾气排放浓度,改善周围环境。
While retaining the native tree species on the site near the residential area, the thickness of the green belt is set to 11 meters to minimize pollution and noise.Plants use the common but rarely used plant toon trees and shrubs in Sichuan countryside to build vertical space and form an ecologically sustainable “island green lung”. Based on plant photosynthesis, the site can produce 3,850 kilograms of oxygen a day, and the car’s carbon emissions are 179.8 kilograms a day. Create ecological microclimate, reduce the concentration of automobile exhaust emissions, improve the surrounding environment.
植物群落微单元
PLANT UNIT
植物特征——模拟雨林生态系统的多层状结构
结构分成:突出层(9m以上);树冠层(2-6m);地被层(0-2m)
结构分成:蓝花楹、栾树、乡土植物椿树,呈高耸伞状,构建高度在9m以上的突出层,多层叶片叠加吸收80%以上并反射10%以上的可见光辐射,通过光合作用,起到第一层拦截作用,对遮阴起到明显的效果;热带属性的杨梅、芭蕉、狐尾椰子、银叶金合欢等,构建高 度在2~6m的树冠层,郁闭的树冠横向生长,吸收阳光和雨水,叶面交错的孔隙让空气过滤与渗透,让热量在流动中消减;地被层被选用绿色系阔叶类植物天堂鸟、圆叶轴榈、矮蒲葵、象耳芋、龟背竹、仙茅、花叶良姜、小天使春羽、黑魔法竹芋、绵毛水苏等,除屏蔽紫外辐射效果更佳外,叶面积指数(指单位土地面积上植物叶片总面积占土地面积的倍数)≥3,丰富的叶片质感和肌理、高覆盖度的下木增强了对小环境的增散作用,形成局部“绿洲效应”。
The structure is divided into: jacaranda, koelluteria, native plant toon tree, which is a towering umbrella, building a protruding layer with a height of more than 9m. The multi-layer leaves superimposed absorb more than 80% and reflect more than 10% of the visible light radiation, and play the first layer interception effect through photosynthesis, which plays an obvious effect on shade. Tropical properties of bayberry, banana, fox tail coconut, silver leaf acacia, etc
寄生吸互:附生植物鹿角蕨、肾蕨、鸟巢蕨、石斛,形成稠密的立体绿网,从视觉和体感上,将“制冷”和“加湿”在场地中加强。场地内的植物,经过5个月的自然生长,在物种优胜劣汰中,完成了自给自足的裂变,在没有过度干预的前提下,形成了完整的生态链条。
Parasitic absorption: Epiphytes staghorn fern, kidney fern, bird’s nest fern, Dendrobium, form a dense three-dimensional green web, visually and physically, to strengthen the “cooling” and “humidification” in the site.The plants in the site, after 5 months of natural growth, completed the self-sufficient fission in the survival of the fittest species, and formed a complete ecological chain without excessive intervention.
去功能标签
NO SIGN
从固有的场域的思维中跳脱,从环境思考维度来重新组织高频使用的公共日常空间,弱化场地的功能画面,用植物转换场地的标签性,让人在日常中体验自然。
It breaks the stereotyped cognition of traditional parking lots, escapes from the inherent thinking of the field, reorganizes the frequently used public daily space from the dimension of environmental thinking, weakens the functional attributes of the site, converts the label of the site with plants, and allows people to experience nature in daily life.
不是结尾的结尾
THE END
我们相信好的设计可以为创造更美丽和宜居的城市做出贡献,这刚好也契合了“公园城市”本身。关于未来的实践,我们更希望这里能作为“Bus Market”的一个可持续空间,赋予场地更多的可能性。
We believe that good design can contribute to the creation of more beautiful and livable cities, which also coincides with the “park city” itself, a concrete manifestation of urban progress.As for the future practice, we hope that this place can be used as a sustainable space of “Bus Market” and give more possibilities to the site.
“项目承载公共交通系统和基础设施改善交通便利性之外,我们带着探索城市公园低碳运维的维度对场地形进行了思考——城市绿地如何成为城市多功能绿色公共空间。”
审稿编辑:junjun
更多 Read more about: 魏玛景观

































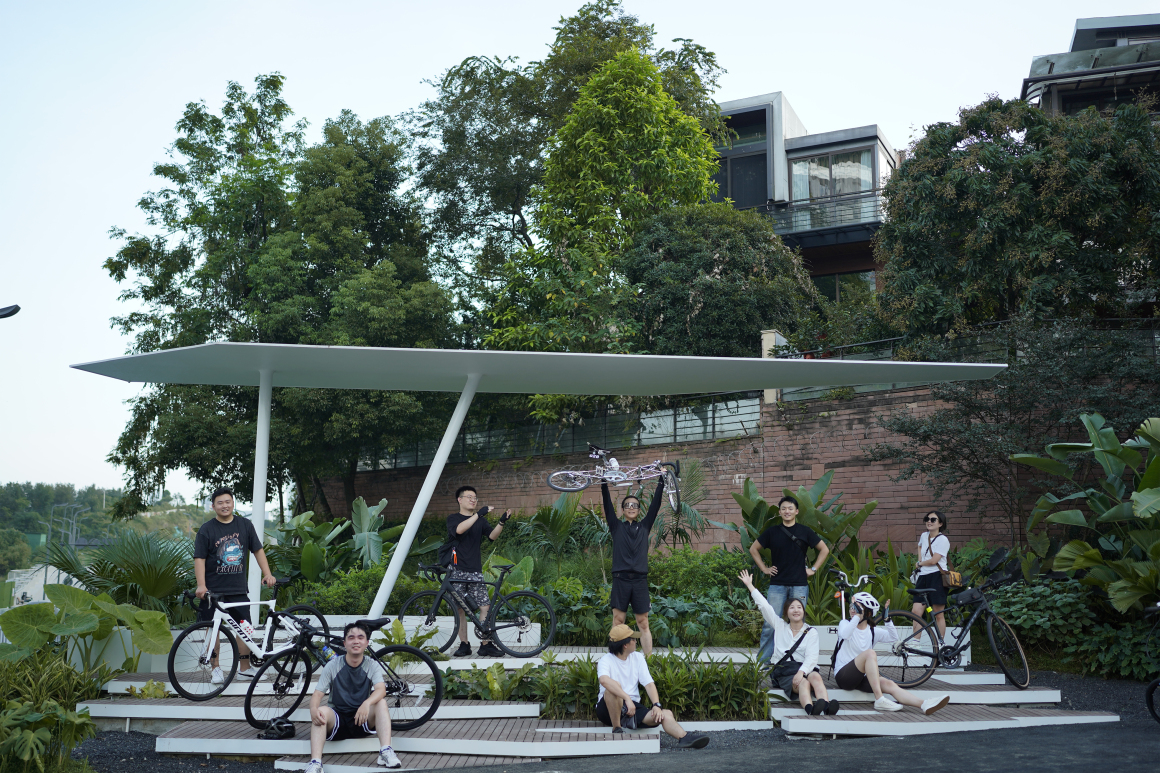



0 Comments